An official website of the United States government
 United States Department of Labor
United States Department of Labor
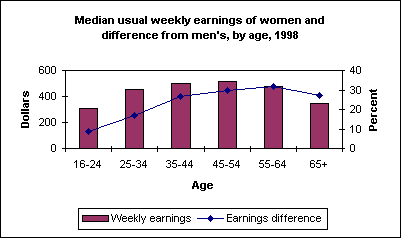
Median weekly earnings of female full-time wage and salary workers were $456 in 1998. This was 76.3 percent of the $598 median for men. Both the level of women’s earnings and the difference from men’s varied considerably by age.
[Chart data—TXT]
Among women, 45- to 54-year-olds had the highest median weekly earnings in 1998 ($516), followed by 35-44 year olds ($498). The difference between women’s and men’s earnings was relatively large among older workers. For workers ages 45 to 54, women’s earnings were 70.5 percent of men’s. Among 55- 64-year olds, the earnings ratio was 68.2 percent.
In contrast, young women and men under the age of 25 had fairly similar earnings. Median weekly earnings for women 16 to 24 years old were $305, roughly 91 percent of the earning of young men of that age.
These earnings data are a product of the Current Population Survey. "Earnings difference" is charted as 100-(Women's earnings as a percent of men's). For more information, see "Highlights of Women’s Earnings," BLS Report 928.
Bureau of Labor Statistics, U.S. Department of Labor, The Economics Daily, Women’s earnings, earnings difference highest after age 45 at https://www.bls.gov/opub/ted/1999/may/wk2/art02.htm (visited September 03, 2025).

