An official website of the United States government
 United States Department of Labor
United States Department of Labor
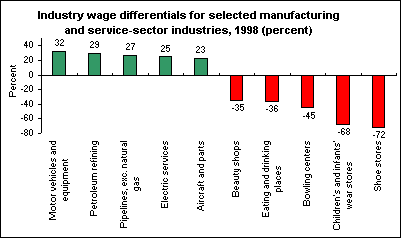
The wages paid to workers in similar occupations but different industries varied substantially in 1998.
[Chart data—TXT]
The chart shows "industry wage differentials" for a number of manufacturing and service-sector industries—the differentials compare wages in the industries shown to wages in the miscellaneous plastics manufacturing industry, controlling for occupational composition.
For example, on average, the wages paid any given occupation in the motor vehicles manufacturing industry are 32 percent higher than those in the miscellaneous plastics industry. At the other end of the spectrum, the wages paid to given occupations in the shoe stores industry were 72 percent below the occupations’ wages in miscellaneous plastics manufacturing.
There are a number of factors that may explain industry wage differentials. Among them are (1) differing levels of skills among workers in given occupations, (2) degree of workers’ exposure to unpleasant, risky, or hazardous workplace conditions, and (3) the use of wage differentials to reduce employee turnover, absenteeism, or shirking.
These data are from the Occupational Employment Statistics program. To find out more about industry wage differentials, see "Interindustry wage differentials: patterns and possible sources," by Jane Osburn, Monthly Labor Review, February 2000. The miscellaneous plastics manufacturing industry was chosen as the base for the differential calculations due to the large number of occupations that are in this industry; otherwise the choice of base is arbitrary.
Bureau of Labor Statistics, U.S. Department of Labor, The Economics Daily, Wage differences among industries at https://www.bls.gov/opub/ted/2000/apr/wk1/art04.htm (visited February 28, 2026).

Recent editions of Spotlight on Statistics
