An official website of the United States government
 United States Department of Labor
United States Department of Labor
Job Openings and Labor Turnover Survey (JOLTS) estimates are based on a national sample of approximately 21,000 establishments. These data are used by policymakers, academics, industry experts, economists, and others to better understand the current state of the U.S. economy and to understand the dynamic activity of businesses in the economy that lead to aggregate employment changes. While the current national sample size is designed to support estimates for major industries at the national level and total nonfarm estimates at the regional level, the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) researched leveraging the sample to produce model-assisted estimates at the state total nonfarm level. We encourage data users to review these estimates and provide input on both the technical aspects of the models and on the usability of the resulting data.
These state estimates are published as a historical series comprised of an annually revised benchmarked historical component (Composite Synthetic model) and a current component (Extended Composite Synthetic model) which provides monthly "real-time" estimates between lagged benchmarks.
JOLTS state estimates contain both published models in the series.
Estimates are available for not seasonally adjusted and seasonally adjusted estimates. As noted, estimates are presented as a combination of Composite Synthetic (CompSyn) and Extended Composite Synthetic (ECompSyn) estimates. More specifically, estimates are from the CompSyn model from December 2000 to December 2023 and uses the ECompSyn model to extend the CompSyn model from January 2024 to current reference month/year. Additionally, the CompSyn model will be updated annually with a full year of data following the release of 16 months of ECompSyn estimates.
Please note that BLS releases these estimates monthly in a press release. The JOLTS state monthly release is approximately two weeks following the JOLTS national release and include the same reference period. We encourage data users to provide input on these data at joltsinfo@bls.gov.
Both models take the following form:
J=w1(D)+w2(M)
Where
J=w1(D)+w2(MS)
Where
Where
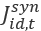 is the Extended Composite Synthetic state industry estimate for month t
is the Extended Composite Synthetic state industry estimate for month t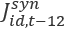 is the Composite Synthetic state industry estimate for month t-12 (one year ago)
is the Composite Synthetic state industry estimate for month t-12 (one year ago)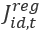 is the Composite Regional state industry estimate for month t
is the Composite Regional state industry estimate for month t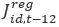 is the Composite Regional state industry estimate for month t-12 (one year ago)
is the Composite Regional state industry estimate for month t-12 (one year ago)The Composite Synthetic state industry estimate from one year ago is extended by adjusting that estimate by the ratio of the current Composite Regional model estimate to the Composite Regional model estimate from one year ago. The Extended Composite Synthetic state industry estimates are summed across industry to form an Extended Composite Synthetic state estimate.
This approach ensures that the extended composite synthetic state estimates reflect current JOLTS regional and industry level economic conditions.
A more complete description of both models is available on the JOLTS State Estimates Methodology page. Some common questions and answers can be found on our Frequently Asked Questions page.
Last Modified Date: July 23, 2025