An official website of the United States government
 United States Department of Labor
United States Department of Labor
Teach courses in communications, such as organizational communications, public relations, radio/television broadcasting, and journalism. Includes both teachers primarily engaged in teaching and those who do a combination of teaching and research.
Employment estimate and mean wage estimates for this occupation:
| Employment (1) | Employment RSE (3) |
Mean hourly wage |
Mean annual wage (2) |
Mean wage RSE (3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 29,120 | 2.1 % | (4) | $79,830 | 1.1 % |
Percentile wage estimates for this occupation:
| Percentile | 10% | 25% | 50% (Median) |
75% | 90% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annual Wage (2) | $38,160 | $51,470 | $70,630 | $97,920 | $137,830 |
Industries with the highest published employment and wages for this occupation are provided. For a list of all industries with employment in this occupation, see the Create Customized Tables function.
Industries with the highest levels of employment in this occupation:
| Industry | Employment (1) | Percent of industry employment | Hourly mean wage | Annual mean wage (2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Colleges, Universities, and Professional Schools | 21,840 | 0.71 | (4) | $77,070 |
| Junior Colleges | 7,190 | 1.01 | (4) | $88,410 |
| Technical and Trade Schools | 50 | 0.04 | (4) | $54,540 |
Industries with the highest concentration of employment in this occupation:
| Industry | Employment (1) | Percent of industry employment | Hourly mean wage | Annual mean wage (2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Junior Colleges | 7,190 | 1.01 | (4) | $88,410 |
| Colleges, Universities, and Professional Schools | 21,840 | 0.71 | (4) | $77,070 |
| Technical and Trade Schools | 50 | 0.04 | (4) | $54,540 |
Top paying industries for this occupation:
| Industry | Employment (1) | Percent of industry employment | Hourly mean wage | Annual mean wage (2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Junior Colleges | 7,190 | 1.01 | (4) | $88,410 |
| Colleges, Universities, and Professional Schools | 21,840 | 0.71 | (4) | $77,070 |
| Technical and Trade Schools | 50 | 0.04 | (4) | $54,540 |
States and areas with the highest published employment, location quotients, and wages for this occupation are provided. For a list of all areas with employment in this occupation, see the Create Customized Tables function.
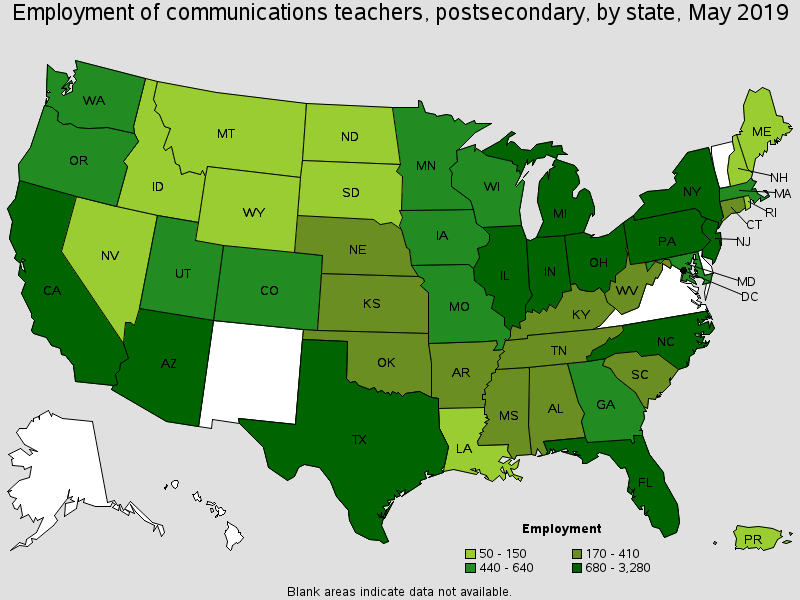
States with the highest employment level in this occupation:
| State | Employment (1) | Employment per thousand jobs | Location quotient (9) | Hourly mean wage | Annual mean wage (2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| New York | 3,280 | 0.34 | 1.74 | (4) | $93,960 |
| Texas | 2,260 | 0.18 | 0.92 | (4) | $62,980 |
| California | 2,170 | 0.13 | 0.63 | (4) | $129,220 |
| Illinois | 1,660 | 0.28 | 1.39 | (4) | $83,190 |
| Pennsylvania | 1,440 | 0.24 | 1.23 | (4) | $78,880 |
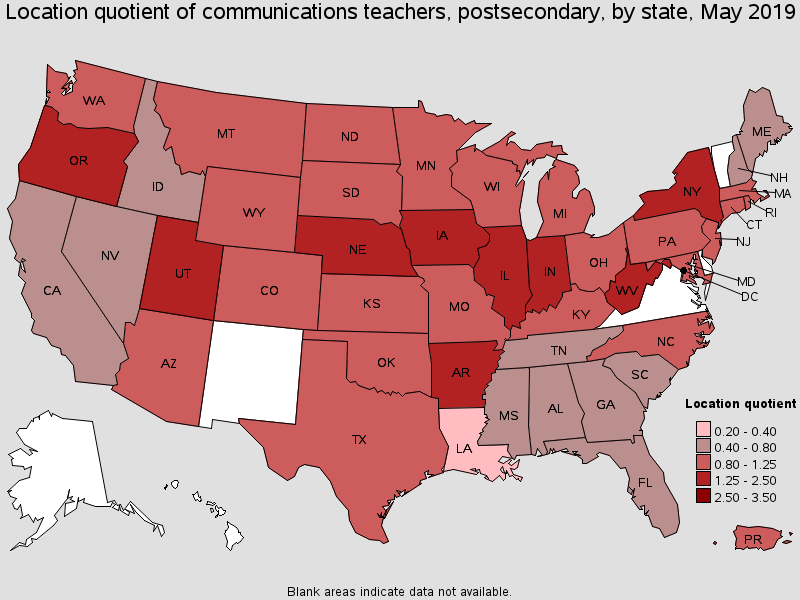
States with the highest concentration of jobs and location quotients in this occupation:
| State | Employment (1) | Employment per thousand jobs | Location quotient (9) | Hourly mean wage | Annual mean wage (2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| District of Columbia | 280 | 0.39 | 1.95 | (4) | $96,590 |
| Iowa | 550 | 0.35 | 1.78 | (4) | $82,520 |
| New York | 3,280 | 0.34 | 1.74 | (4) | $93,960 |
| Arkansas | 410 | 0.34 | 1.71 | (4) | $57,160 |
| Indiana | 970 | 0.32 | 1.59 | (4) | $72,050 |
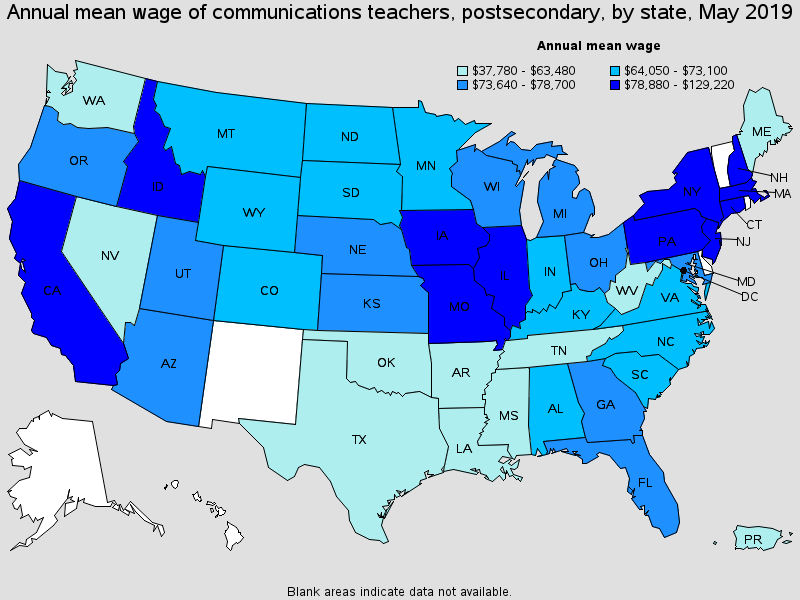
Top paying States for this occupation:
| State | Employment (1) | Employment per thousand jobs | Location quotient (9) | Hourly mean wage | Annual mean wage (2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| California | 2,170 | 0.13 | 0.63 | (4) | $129,220 |
| District of Columbia | 280 | 0.39 | 1.95 | (4) | $96,590 |
| New York | 3,280 | 0.34 | 1.74 | (4) | $93,960 |
| New Jersey | 970 | 0.24 | 1.20 | (4) | $92,290 |
| Massachusetts | 600 | 0.17 | 0.84 | (4) | $88,660 |
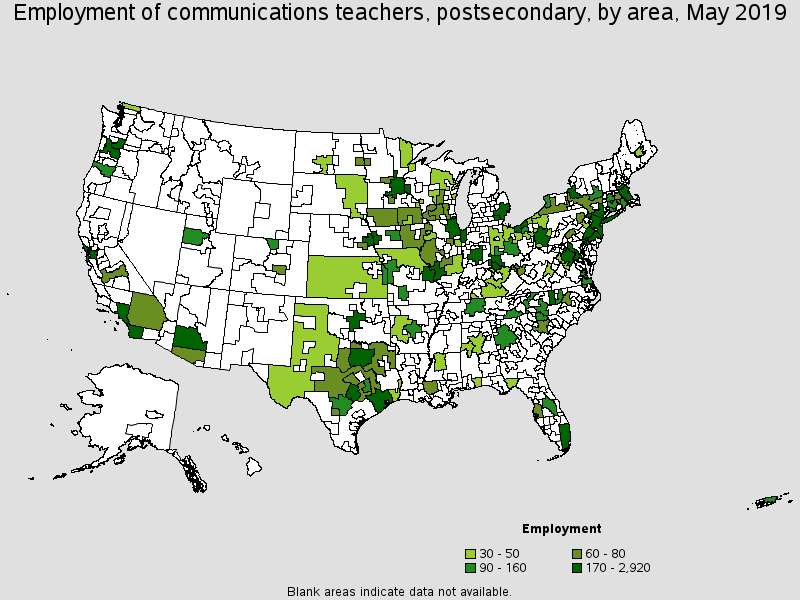
Metropolitan areas with the highest employment level in this occupation:
| Metropolitan area | Employment (1) | Employment per thousand jobs | Location quotient (9) | Hourly mean wage | Annual mean wage (2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| New York-Newark-Jersey City, NY-NJ-PA | 2,920 | 0.30 | 1.52 | (4) | $99,080 |
| Chicago-Naperville-Elgin, IL-IN-WI | 1,410 | 0.30 | 1.52 | (4) | $83,350 |
| Los Angeles-Long Beach-Anaheim, CA | 1,100 | 0.18 | 0.89 | (4) | $139,590 |
| Philadelphia-Camden-Wilmington, PA-NJ-DE-MD | 930 | 0.32 | 1.63 | (4) | $91,820 |
| Washington-Arlington-Alexandria, DC-VA-MD-WV | 890 | 0.28 | 1.41 | (4) | $79,180 |
| Phoenix-Mesa-Scottsdale, AZ | 500 | 0.24 | 1.19 | (8) | (8) |
| Dallas-Fort Worth-Arlington, TX | 450 | 0.12 | 0.62 | (4) | $54,230 |
| Houston-The Woodlands-Sugar Land, TX | 450 | 0.15 | 0.74 | (4) | $70,820 |
| Indianapolis-Carmel-Anderson, IN | 420 | 0.40 | 2.01 | (8) | (8) |
| Syracuse, NY | 410 | 1.35 | 6.82 | (4) | $82,950 |
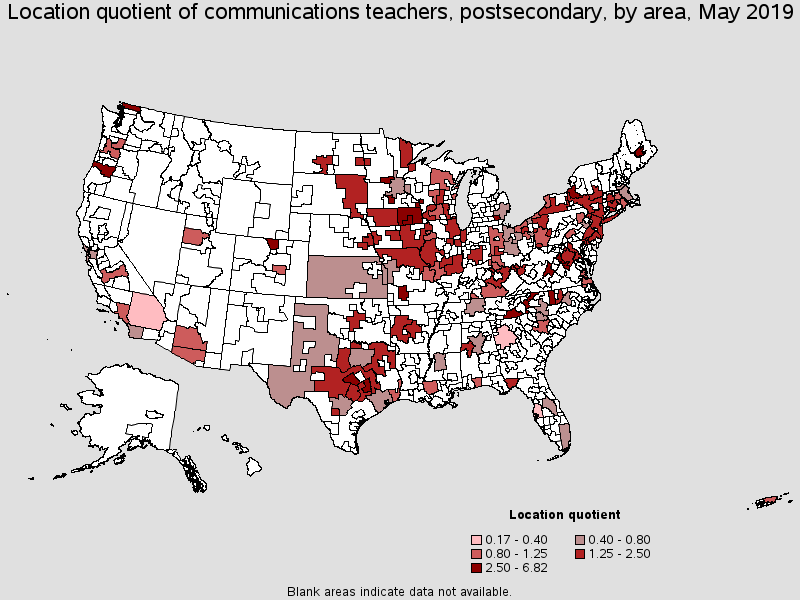
Metropolitan areas with the highest concentration of jobs and location quotients in this occupation:
| Metropolitan area | Employment (1) | Employment per thousand jobs | Location quotient (9) | Hourly mean wage | Annual mean wage (2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Syracuse, NY | 410 | 1.35 | 6.82 | (4) | $82,950 |
| Mankato-North Mankato, MN | 60 | 1.10 | 5.54 | (8) | (8) |
| Ann Arbor, MI | 230 | 1.04 | 5.26 | (4) | $69,690 |
| College Station-Bryan, TX | 90 | 0.81 | 4.09 | (4) | $88,890 |
| Eugene, OR | 120 | 0.79 | 4.00 | (4) | $85,600 |
| St. Cloud, MN | 80 | 0.76 | 3.81 | (4) | $76,430 |
| Bangor, ME | 50 | 0.74 | 3.74 | (4) | $60,080 |
| Springfield, MO | 150 | 0.72 | 3.64 | (8) | (8) |
| Waterloo-Cedar Falls, IA | 50 | 0.60 | 3.05 | (4) | $72,450 |
| Bellingham, WA | 50 | 0.58 | 2.94 | (4) | $72,510 |
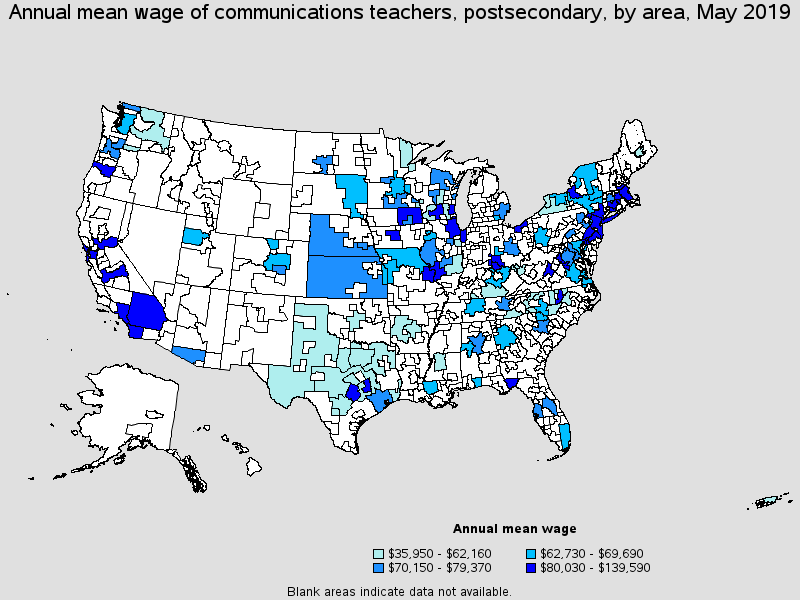
Top paying metropolitan areas for this occupation:
| Metropolitan area | Employment (1) | Employment per thousand jobs | Location quotient (9) | Hourly mean wage | Annual mean wage (2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Los Angeles-Long Beach-Anaheim, CA | 1,100 | 0.18 | 0.89 | (4) | $139,590 |
| San Francisco-Oakland-Hayward, CA | 210 | 0.08 | 0.42 | (4) | $128,640 |
| San Diego-Carlsbad, CA | 200 | 0.14 | 0.68 | (4) | $124,400 |
| Fresno, CA | 60 | 0.16 | 0.83 | (4) | $120,510 |
| Riverside-San Bernardino-Ontario, CA | 80 | 0.05 | 0.26 | (4) | $109,610 |
| Sacramento--Roseville--Arden-Arcade, CA | (8) | (8) | (8) | (4) | $108,920 |
| New York-Newark-Jersey City, NY-NJ-PA | 2,920 | 0.30 | 1.52 | (4) | $99,080 |
| Des Moines-West Des Moines, IA | 90 | 0.25 | 1.25 | (4) | $92,340 |
| Philadelphia-Camden-Wilmington, PA-NJ-DE-MD | 930 | 0.32 | 1.63 | (4) | $91,820 |
| Worcester, MA-CT | 60 | 0.21 | 1.08 | (4) | $91,770 |
Nonmetropolitan areas with the highest employment in this occupation:
| Nonmetropolitan area | Employment (1) | Employment per thousand jobs | Location quotient (9) | Hourly mean wage | Annual mean wage (2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mountain North Carolina nonmetropolitan area | 110 | 0.88 | 4.45 | (4) | $61,100 |
| North Texas Region of Texas nonmetropolitan area | 80 | 0.30 | 1.53 | (4) | $38,130 |
| Central East New York nonmetropolitan area | 80 | 0.48 | 2.41 | (4) | $65,890 |
| Northeast Iowa nonmetropolitan area | 80 | 0.75 | 3.77 | (4) | $93,070 |
| Hill Country Region of Texas nonmetropolitan area | 60 | 0.32 | 1.64 | (4) | $50,820 |
Nonmetropolitan areas with the highest concentration of jobs and location quotients in this occupation:
| Nonmetropolitan area | Employment (1) | Employment per thousand jobs | Location quotient (9) | Hourly mean wage | Annual mean wage (2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mountain North Carolina nonmetropolitan area | 110 | 0.88 | 4.45 | (4) | $61,100 |
| Northwest Virginia nonmetropolitan area | 50 | 0.85 | 4.29 | (4) | $80,520 |
| Northeast Iowa nonmetropolitan area | 80 | 0.75 | 3.77 | (4) | $93,070 |
| Central East New York nonmetropolitan area | 80 | 0.48 | 2.41 | (4) | $65,890 |
| North Missouri nonmetropolitan area | 50 | 0.47 | 2.36 | (4) | $64,310 |
Top paying nonmetropolitan areas for this occupation:
| Nonmetropolitan area | Employment (1) | Employment per thousand jobs | Location quotient (9) | Hourly mean wage | Annual mean wage (2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Northeast Iowa nonmetropolitan area | 80 | 0.75 | 3.77 | (4) | $93,070 |
| Northwest Virginia nonmetropolitan area | 50 | 0.85 | 4.29 | (4) | $80,520 |
| West Central Illinois nonmetropolitan area | 60 | 0.36 | 1.79 | (4) | $78,650 |
| South Nebraska nonmetropolitan area | (8) | (8) | (8) | (4) | $74,450 |
| Southeast Minnesota nonmetropolitan area | (8) | (8) | (8) | (4) | $74,360 |
These estimates are calculated with data collected from employers in all industry sectors, all metropolitan and nonmetropolitan areas, and all states and the District of Columbia. The top employment and wage figures are provided above. The complete list is available in the downloadable XLS files.
The percentile wage estimate is the value of a wage below which a certain percent of workers fall. The median wage is the 50th percentile wage estimate--50 percent of workers earn less than the median and 50 percent of workers earn more than the median. More about percentile wages.
(1) Estimates for detailed occupations do not sum to the totals because the totals include occupations not shown separately. Estimates do not include self-employed workers.
(2) Annual wages have been calculated by multiplying the hourly mean wage by a "year-round, full-time" hours figure of 2,080 hours; for those occupations where there is not an hourly wage published, the annual wage has been directly calculated from the reported survey data.
(3) The relative standard error (RSE) is a measure of the reliability of a survey statistic. The smaller the relative standard error, the more precise the estimate.
(4) Wages for some occupations that do not generally work year-round, full time, are reported either as hourly wages or annual salaries depending on how they are typically paid.
(8) Estimate not released.
(9) The location quotient is the ratio of the area concentration of occupational employment to the national average concentration. A location quotient greater than one indicates the occupation has a higher share of employment than average, and a location quotient less than one indicates the occupation is less prevalent in the area than average.
Other OES estimates and related information:
May 2019 National Occupational Employment and Wage Estimates
May 2019 State Occupational Employment and Wage Estimates
May 2019 Metropolitan and Nonmetropolitan Area Occupational Employment and Wage Estimates
May 2019 National Industry-Specific Occupational Employment and Wage Estimates
Last Modified Date: July 6, 2020