An official website of the United States government
 United States Department of Labor
United States Department of Labor
Manage public and private forested lands for economic, recreational, and conservation purposes. May inventory the type, amount, and location of standing timber, appraise the timber's worth, negotiate the purchase, and draw up contracts for procurement. May determine how to conserve wildlife habitats, creek beds, water quality, and soil stability, and how best to comply with environmental regulations. May devise plans for planting and growing new trees, monitor trees for healthy growth, and determine optimal harvesting schedules.
Employment estimate and mean wage estimates for Foresters:
| Employment (1) | Employment RSE (3) |
Mean hourly wage |
Mean annual wage (2) |
Wage RSE (3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9,360 | 3.9 % | $ 31.73 | $ 66,000 | 1.3 % |
Percentile wage estimates for Foresters:
| Percentile | 10% | 25% | 50% (Median) |
75% | 90% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hourly Wage | $ 20.43 | $ 24.95 | $ 30.76 | $ 37.03 | $ 44.74 |
| Annual Wage (2) | $ 42,500 | $ 51,890 | $ 63,980 | $ 77,010 | $ 93,060 |
Industries with the highest published employment and wages for Foresters are provided. For a list of all industries with employment in Foresters, see the Create Customized Tables function.
Industries with the highest levels of employment in Foresters:
| Industry | Employment (1) | Percent of industry employment | Hourly mean wage | Annual mean wage (2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| State Government, excluding schools and hospitals (OEWS Designation) | 3,050 | 0.14 | $ 29.63 | $ 61,640 |
| Federal Executive Branch (OEWS Designation) | 1,300 | 0.06 | $ 32.57 | $ 67,750 |
| Local Government, excluding schools and hospitals (OEWS Designation) | 1,140 | 0.02 | $ 30.92 | $ 64,320 |
| Logging | 1,120 | 2.33 | $ 33.66 | $ 70,000 |
| Management, Scientific, and Technical Consulting Services | 760 | 0.05 | $ 32.05 | $ 66,660 |
Industries with the highest concentration of employment in Foresters:
| Industry | Employment (1) | Percent of industry employment | Hourly mean wage | Annual mean wage (2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Logging | 1,120 | 2.33 | $ 33.66 | $ 70,000 |
| Sawmills and Wood Preservation | 550 | 0.62 | $ 34.82 | $ 72,430 |
| Pulp, Paper, and Paperboard Mills | 150 | 0.16 | $ 30.64 | $ 63,720 |
| State Government, excluding schools and hospitals (OEWS Designation) | 3,050 | 0.14 | $ 29.63 | $ 61,640 |
| Electric Power Generation, Transmission and Distribution | 450 | 0.12 | $ 38.40 | $ 79,870 |
Top paying industries for Foresters:
| Industry | Employment (1) | Percent of industry employment | Hourly mean wage | Annual mean wage (2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Real Estate | (8) | (8) | $ 40.60 | $ 84,450 |
| Electric Power Generation, Transmission and Distribution | 450 | 0.12 | $ 38.40 | $ 79,870 |
| Sawmills and Wood Preservation | 550 | 0.62 | $ 34.82 | $ 72,430 |
| Logging | 1,120 | 2.33 | $ 33.66 | $ 70,000 |
| Federal Executive Branch (OEWS Designation) | 1,300 | 0.06 | $ 32.57 | $ 67,750 |
States and areas with the highest published employment, location quotients, and wages for Foresters are provided. For a list of all areas with employment in Foresters, see the Create Customized Tables function.
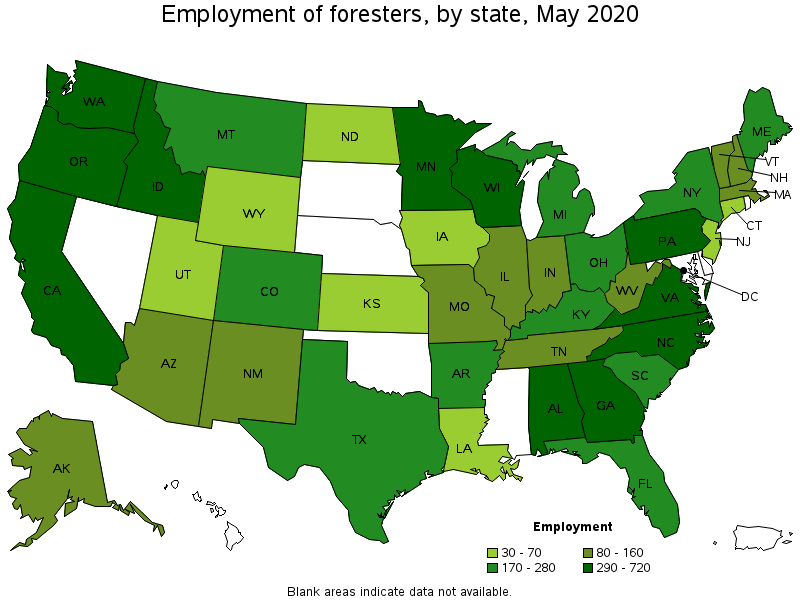
States with the highest employment level in Foresters:
| State | Employment (1) | Employment per thousand jobs | Location quotient (9) | Hourly mean wage | Annual mean wage (2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| California | 720 | 0.04 | 0.65 | $ 38.54 | $ 80,160 |
| Oregon | 680 | 0.38 | 5.58 | $ 34.54 | $ 71,830 |
| Wisconsin | 540 | 0.20 | 2.94 | $ 28.26 | $ 58,780 |
| Washington | 430 | 0.14 | 2.01 | $ 33.52 | $ 69,710 |
| Georgia | 410 | 0.10 | 1.42 | $ 29.97 | $ 62,340 |
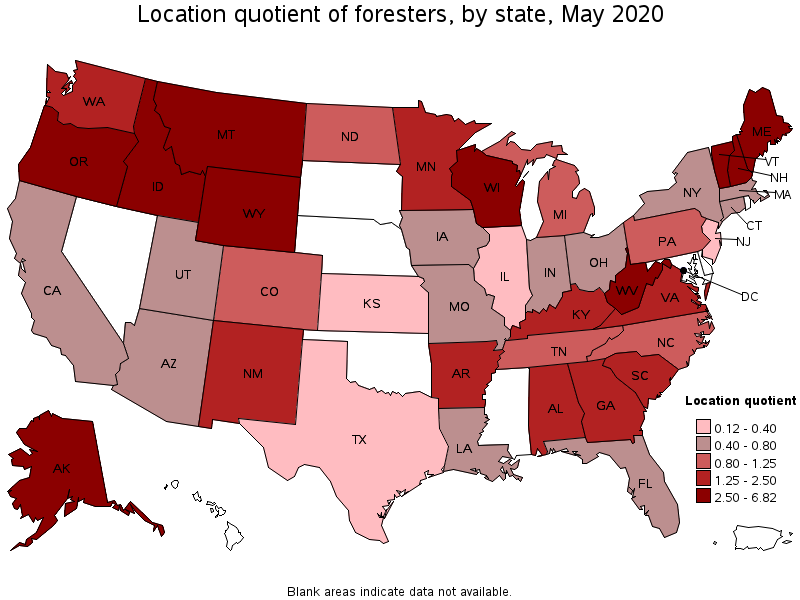
States with the highest concentration of jobs and location quotients in Foresters:
| State | Employment (1) | Employment per thousand jobs | Location quotient (9) | Hourly mean wage | Annual mean wage (2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Montana | 210 | 0.46 | 6.82 | $ 28.43 | $ 59,130 |
| Idaho | 290 | 0.40 | 6.02 | $ 28.55 | $ 59,380 |
| Oregon | 680 | 0.38 | 5.58 | $ 34.54 | $ 71,830 |
| Maine | 170 | 0.30 | 4.48 | (8) | (8) |
| Vermont | 80 | 0.30 | 4.40 | $ 30.50 | $ 63,430 |
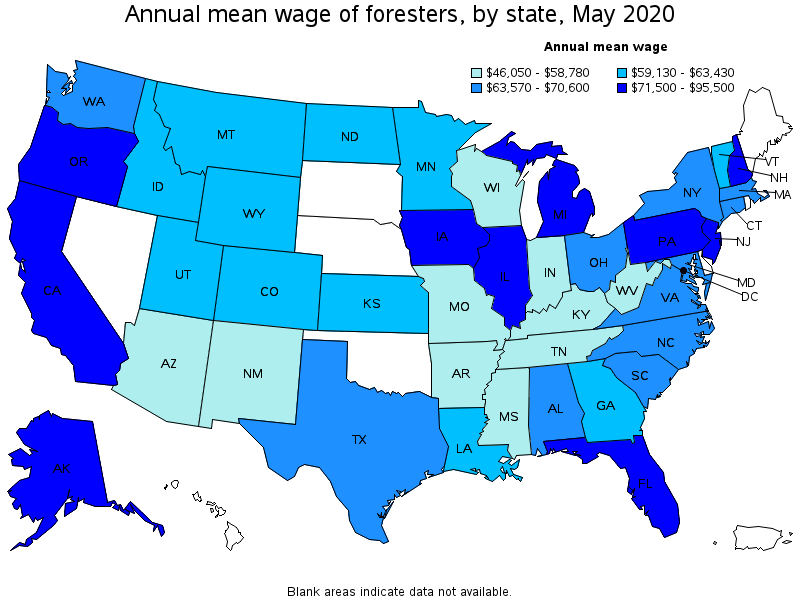
Top paying states for Foresters:
| State | Employment (1) | Employment per thousand jobs | Location quotient (9) | Hourly mean wage | Annual mean wage (2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| District of Columbia | 40 | 0.05 | 0.77 | $ 45.92 | $ 95,500 |
| New Jersey | 30 | 0.01 | 0.12 | $ 39.04 | $ 81,200 |
| California | 720 | 0.04 | 0.65 | $ 38.54 | $ 80,160 |
| Alaska | 80 | 0.26 | 3.88 | $ 36.60 | $ 76,120 |
| Florida | 230 | 0.03 | 0.40 | $ 36.48 | $ 75,880 |
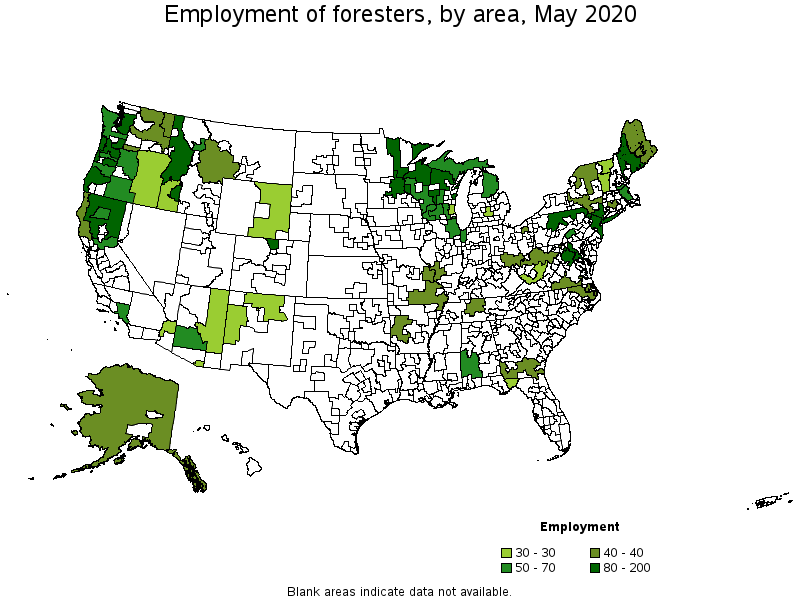
Metropolitan areas with the highest employment level in Foresters:
| Metropolitan area | Employment (1) | Employment per thousand jobs | Location quotient (9) | Hourly mean wage | Annual mean wage (2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seattle-Tacoma-Bellevue, WA | 160 | 0.08 | 1.19 | $ 33.23 | $ 69,110 |
| Minneapolis-St. Paul-Bloomington, MN-WI | 110 | 0.06 | 0.92 | $ 30.07 | $ 62,550 |
| Washington-Arlington-Alexandria, DC-VA-MD-WV | 110 | 0.03 | 0.52 | $ 38.45 | $ 79,970 |
| Albany, OR | 90 | 2.11 | 31.34 | $ 37.10 | $ 77,180 |
| New York-Newark-Jersey City, NY-NJ-PA | 80 | 0.01 | 0.14 | $ 32.40 | $ 67,390 |
| Portland-Vancouver-Hillsboro, OR-WA | 80 | 0.07 | 1.00 | $ 36.31 | $ 75,520 |
| Fort Collins, CO | 80 | 0.49 | 7.31 | $ 26.30 | $ 54,710 |
| Salem, OR | 70 | 0.43 | 6.45 | $ 37.01 | $ 76,970 |
| Chicago-Naperville-Elgin, IL-IN-WI | 70 | 0.01 | 0.22 | $ 36.86 | $ 76,670 |
| Eugene, OR | 60 | 0.42 | 6.26 | $ 33.24 | $ 69,140 |
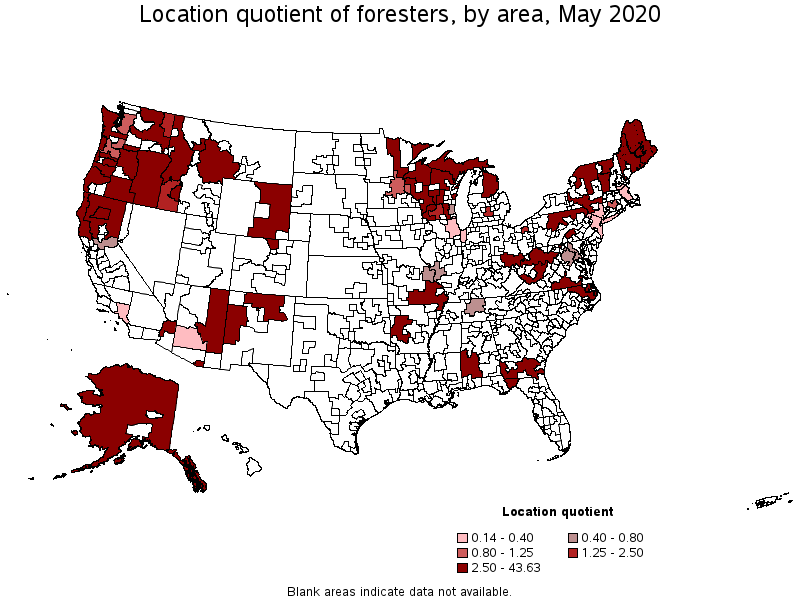
Metropolitan areas with the highest concentration of jobs and location quotients in Foresters:
| Metropolitan area | Employment (1) | Employment per thousand jobs | Location quotient (9) | Hourly mean wage | Annual mean wage (2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Albany, OR | 90 | 2.11 | 31.34 | $ 37.10 | $ 77,180 |
| Missoula, MT | 50 | 0.80 | 11.81 | $ 28.44 | $ 59,150 |
| Redding, CA | 50 | 0.72 | 10.74 | $ 42.78 | $ 88,980 |
| Bangor, ME | 40 | 0.72 | 10.70 | $ 42.98 | $ 89,400 |
| Fort Collins, CO | 80 | 0.49 | 7.31 | $ 26.30 | $ 54,710 |
| Salem, OR | 70 | 0.43 | 6.45 | $ 37.01 | $ 76,970 |
| Eugene, OR | 60 | 0.42 | 6.26 | $ 33.24 | $ 69,140 |
| Tallahassee, FL | 30 | 0.18 | 2.63 | $ 28.62 | $ 59,530 |
| Harrisburg-Carlisle, PA | 50 | 0.17 | 2.54 | $ 35.50 | $ 73,840 |
| Lansing-East Lansing, MI | 30 | 0.16 | 2.44 | $ 35.70 | $ 74,250 |
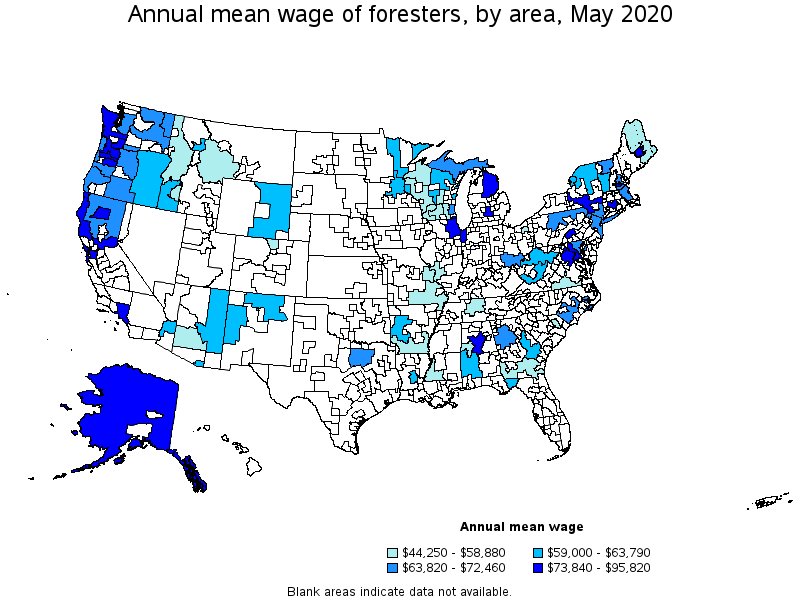
Top paying metropolitan areas for Foresters:
| Metropolitan area | Employment (1) | Employment per thousand jobs | Location quotient (9) | Hourly mean wage | Annual mean wage (2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| San Francisco-Oakland-Hayward, CA | (8) | (8) | (8) | $ 46.07 | $ 95,820 |
| Sacramento--Roseville--Arden-Arcade, CA | 50 | 0.05 | 0.78 | $ 44.72 | $ 93,020 |
| Bangor, ME | 40 | 0.72 | 10.70 | $ 42.98 | $ 89,400 |
| Redding, CA | 50 | 0.72 | 10.74 | $ 42.78 | $ 88,980 |
| Manchester, NH | (8) | (8) | (8) | $ 42.14 | $ 87,650 |
| Los Angeles-Long Beach-Anaheim, CA | 50 | 0.01 | 0.14 | $ 41.17 | $ 85,640 |
| Washington-Arlington-Alexandria, DC-VA-MD-WV | 110 | 0.03 | 0.52 | $ 38.45 | $ 79,970 |
| Birmingham-Hoover, AL | (8) | (8) | (8) | $ 37.57 | $ 78,150 |
| Albany, OR | 90 | 2.11 | 31.34 | $ 37.10 | $ 77,180 |
| Salem, OR | 70 | 0.43 | 6.45 | $ 37.01 | $ 76,970 |
Nonmetropolitan areas with the highest employment in Foresters:
| Nonmetropolitan area | Employment (1) | Employment per thousand jobs | Location quotient (9) | Hourly mean wage | Annual mean wage (2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Northwestern Idaho nonmetropolitan area | 200 | 2.94 | 43.63 | $ 28.24 | $ 58,730 |
| Coast Oregon nonmetropolitan area | 150 | 1.38 | 20.50 | $ 31.94 | $ 66,440 |
| Northeastern Wisconsin nonmetropolitan area | 140 | 0.75 | 11.20 | $ 28.54 | $ 59,350 |
| Northwestern Wisconsin nonmetropolitan area | 100 | 2.09 | 31.10 | $ 27.97 | $ 58,180 |
| Southwest Maine nonmetropolitan area | 90 | 0.49 | 7.26 | (8) | (8) |
Nonmetropolitan areas with the highest concentration of jobs and location quotients in Foresters:
| Nonmetropolitan area | Employment (1) | Employment per thousand jobs | Location quotient (9) | Hourly mean wage | Annual mean wage (2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Northwestern Idaho nonmetropolitan area | 200 | 2.94 | 43.63 | $ 28.24 | $ 58,730 |
| Northwestern Wisconsin nonmetropolitan area | 100 | 2.09 | 31.10 | $ 27.97 | $ 58,180 |
| Northeast Minnesota nonmetropolitan area | 80 | 1.93 | 28.60 | $ 29.69 | $ 61,750 |
| Coast Oregon nonmetropolitan area | 150 | 1.38 | 20.50 | $ 31.94 | $ 66,440 |
| Central Oregon nonmetropolitan area | 70 | 1.27 | 18.80 | $ 33.16 | $ 68,970 |
Top paying nonmetropolitan areas for Foresters:
| Nonmetropolitan area | Employment (1) | Employment per thousand jobs | Location quotient (9) | Hourly mean wage | Annual mean wage (2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| North Coast Region of California nonmetropolitan area | 40 | 0.42 | 6.25 | $ 42.99 | $ 89,420 |
| Northeast Lower Peninsula of Michigan nonmetropolitan area | 50 | 0.80 | 11.89 | $ 38.18 | $ 79,410 |
| Central East New York nonmetropolitan area | 40 | 0.24 | 3.64 | $ 37.98 | $ 79,000 |
| Alaska nonmetropolitan area | 40 | 0.41 | 6.13 | $ 36.26 | $ 75,420 |
| Western Washington nonmetropolitan area | 70 | 0.56 | 8.26 | $ 35.51 | $ 73,860 |
These estimates are calculated with data collected from employers in all industry sectors, all metropolitan and nonmetropolitan areas, and all states and the District of Columbia. The top employment and wage figures are provided above. The complete list is available in the downloadable XLS files.
The percentile wage estimate is the value of a wage below which a certain percent of workers fall. The median wage is the 50th percentile wage estimate—50 percent of workers earn less than the median and 50 percent of workers earn more than the median. More about percentile wages.
(1) Estimates for detailed occupations do not sum to the totals because the totals include occupations not shown separately. Estimates do not include self-employed workers.
(2) Annual wages have been calculated by multiplying the hourly mean wage by a "year-round, full-time" hours figure of 2,080 hours; for those occupations where there is not an hourly wage published, the annual wage has been directly calculated from the reported survey data.
(3) The relative standard error (RSE) is a measure of the reliability of a survey statistic. The smaller the relative standard error, the more precise the estimate.
(8) Estimate not released.
(9) The location quotient is the ratio of the area concentration of occupational employment to the national average concentration. A location quotient greater than one indicates the occupation has a higher share of employment than average, and a location quotient less than one indicates the occupation is less prevalent in the area than average.
Other OEWS estimates and related information:
May 2020 National Occupational Employment and Wage Estimates
May 2020 State Occupational Employment and Wage Estimates
May 2020 Metropolitan and Nonmetropolitan Area Occupational Employment and Wage Estimates
May 2020 National Industry-Specific Occupational Employment and Wage Estimates
Last Modified Date: March 31, 2021