An official website of the United States government
 United States Department of Labor
United States Department of Labor
Set up, operate, or tend machines to crush, grind, or polish materials, such as coal, glass, grain, stone, food, or rubber.
Employment estimate and mean wage estimates for Crushing, Grinding, and Polishing Machine Setters, Operators, and Tenders:
| Employment (1) | Employment RSE (3) |
Mean hourly wage |
Mean annual wage (2) |
Wage RSE (3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 27,320 | 2.1 % | $ 21.79 | $ 45,310 | 0.7 % |
Percentile wage estimates for Crushing, Grinding, and Polishing Machine Setters, Operators, and Tenders:
| Percentile | 10% | 25% | 50% (Median) |
75% | 90% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hourly Wage | $ 14.53 | $ 17.26 | $ 20.81 | $ 24.98 | $ 30.52 |
| Annual Wage (2) | $ 30,220 | $ 35,910 | $ 43,290 | $ 51,960 | $ 63,490 |
Industries with the highest published employment and wages for Crushing, Grinding, and Polishing Machine Setters, Operators, and Tenders are provided. For a list of all industries with employment in Crushing, Grinding, and Polishing Machine Setters, Operators, and Tenders, see the Create Customized Tables function.
Industries with the highest levels of employment in Crushing, Grinding, and Polishing Machine Setters, Operators, and Tenders:
| Industry | Employment (1) | Percent of industry employment | Hourly mean wage | Annual mean wage (2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nonmetallic Mineral Product Manufacturing | 4,230 | 1.03 | $ 21.63 | $ 44,980 |
| Nonmetallic Mineral Mining and Quarrying | 3,430 | 3.56 | $ 24.26 | $ 50,470 |
| Grain and Oilseed Milling | 3,000 | 4.78 | $ 22.55 | $ 46,900 |
| Merchant Wholesalers, Durable Goods (4232, 4233, 4235, 4236, 4237, and 4239 only) | 1,090 | 0.08 | $ 21.93 | $ 45,620 |
| Animal Slaughtering and Processing | 1,060 | 0.20 | $ 18.09 | $ 37,630 |
Industries with the highest concentration of employment in Crushing, Grinding, and Polishing Machine Setters, Operators, and Tenders:
| Industry | Employment (1) | Percent of industry employment | Hourly mean wage | Annual mean wage (2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grain and Oilseed Milling | 3,000 | 4.78 | $ 22.55 | $ 46,900 |
| Nonmetallic Mineral Mining and Quarrying | 3,430 | 3.56 | $ 24.26 | $ 50,470 |
| Metal Ore Mining | 990 | 2.35 | $ 29.53 | $ 61,420 |
| Animal Food Manufacturing | 750 | 1.07 | $ 18.44 | $ 38,350 |
| Nonmetallic Mineral Product Manufacturing | 4,230 | 1.03 | $ 21.63 | $ 44,980 |
Top paying industries for Crushing, Grinding, and Polishing Machine Setters, Operators, and Tenders:
| Industry | Employment (1) | Percent of industry employment | Hourly mean wage | Annual mean wage (2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Petroleum and Coal Products Manufacturing | 270 | 0.26 | $ 30.10 | $ 62,600 |
| Coal Mining | 310 | 0.78 | $ 29.71 | $ 61,790 |
| Metal Ore Mining | 990 | 2.35 | $ 29.53 | $ 61,420 |
| Pulp, Paper, and Paperboard Mills | 430 | 0.50 | $ 28.72 | $ 59,740 |
| Electric Power Generation, Transmission and Distribution | 140 | 0.04 | $ 28.16 | $ 58,580 |
States and areas with the highest published employment, location quotients, and wages for Crushing, Grinding, and Polishing Machine Setters, Operators, and Tenders are provided. For a list of all areas with employment in Crushing, Grinding, and Polishing Machine Setters, Operators, and Tenders, see the Create Customized Tables function.
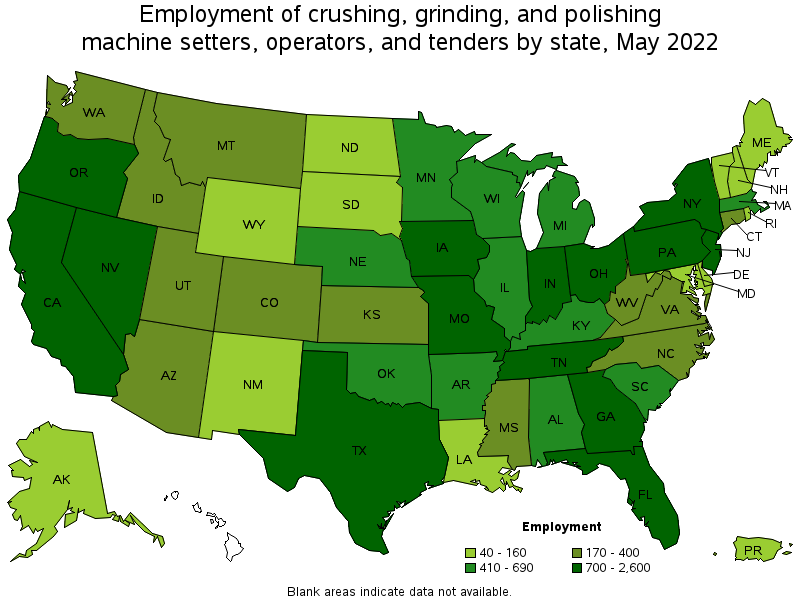
States with the highest employment level in Crushing, Grinding, and Polishing Machine Setters, Operators, and Tenders:
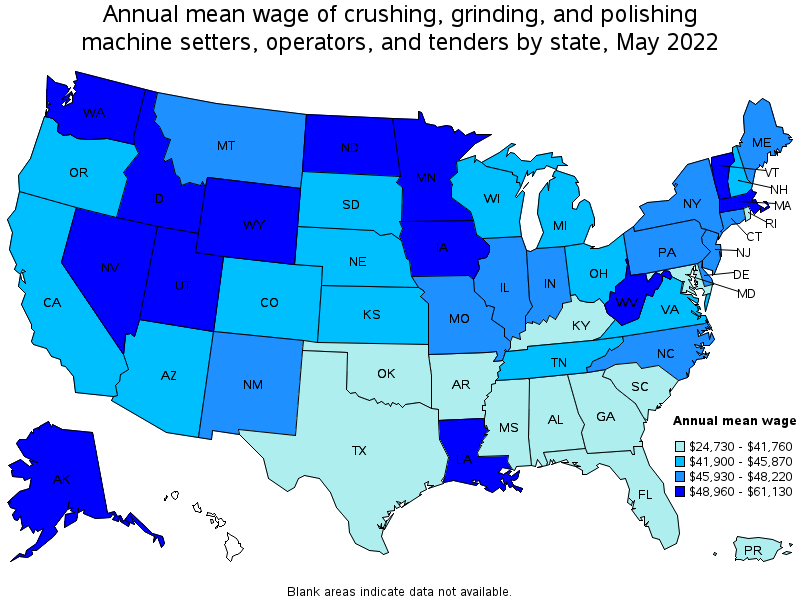
| State | Employment (1) | Employment per thousand jobs | Location quotient (9) | Hourly mean wage | Annual mean wage (2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| California | 2,600 | 0.15 | 0.80 | $ 21.25 | $ 44,190 |
| Texas | 2,350 | 0.18 | 0.98 | $ 19.06 | $ 39,650 |
| Indiana | 1,600 | 0.52 | 2.81 | $ 22.42 | $ 46,630 |
| Pennsylvania | 1,420 | 0.24 | 1.33 | $ 22.62 | $ 47,050 |
| New York | 1,310 | 0.14 | 0.78 | $ 22.69 | $ 47,200 |
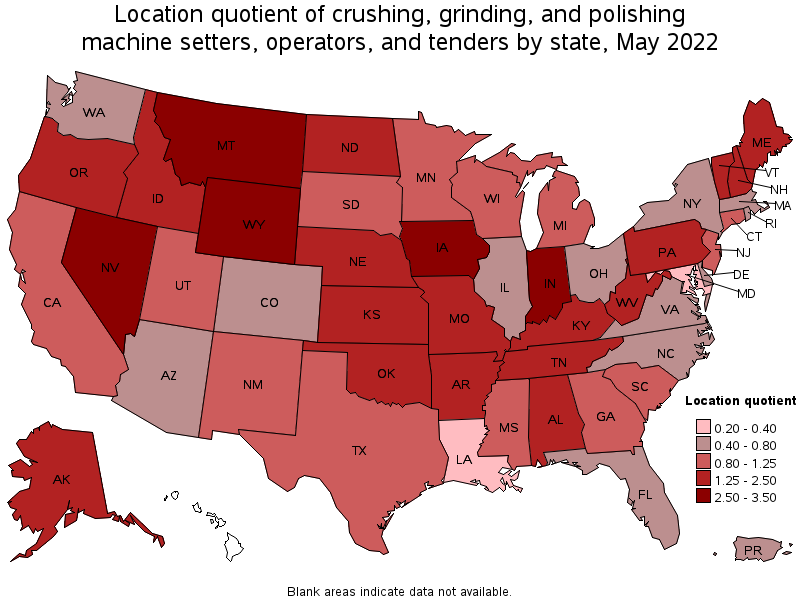
States with the highest concentration of jobs and location quotients in Crushing, Grinding, and Polishing Machine Setters, Operators, and Tenders:
| State | Employment (1) | Employment per thousand jobs | Location quotient (9) | Hourly mean wage | Annual mean wage (2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Montana | 300 | 0.61 | 3.28 | $ 22.64 | $ 47,090 |
| Iowa | 880 | 0.58 | 3.14 | $ 23.93 | $ 49,780 |
| Wyoming | 140 | 0.53 | 2.86 | $ 29.39 | $ 61,130 |
| Indiana | 1,600 | 0.52 | 2.81 | $ 22.42 | $ 46,630 |
| Nevada | 700 | 0.49 | 2.68 | $ 28.80 | $ 59,910 |
Top paying states for Crushing, Grinding, and Polishing Machine Setters, Operators, and Tenders:
| State | Employment (1) | Employment per thousand jobs | Location quotient (9) | Hourly mean wage | Annual mean wage (2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wyoming | 140 | 0.53 | 2.86 | $ 29.39 | $ 61,130 |
| Nevada | 700 | 0.49 | 2.68 | $ 28.80 | $ 59,910 |
| Alaska | 80 | 0.28 | 1.50 | $ 28.11 | $ 58,480 |
| West Virginia | 230 | 0.34 | 1.86 | $ 28.08 | $ 58,400 |
| Minnesota | 640 | 0.23 | 1.23 | $ 27.22 | $ 56,620 |
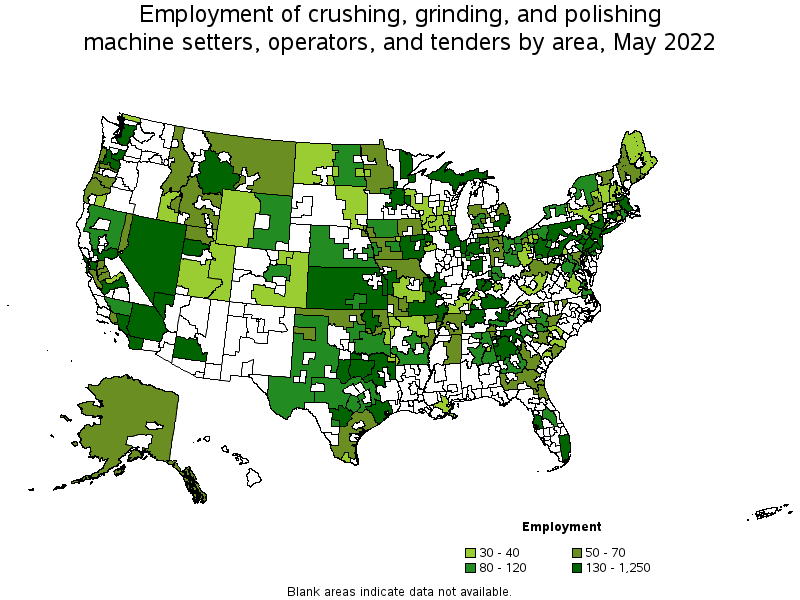
Metropolitan areas with the highest employment level in Crushing, Grinding, and Polishing Machine Setters, Operators, and Tenders:
| Metropolitan area | Employment (1) | Employment per thousand jobs | Location quotient (9) | Hourly mean wage | Annual mean wage (2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| New York-Newark-Jersey City, NY-NJ-PA | 1,250 | 0.14 | 0.74 | $ 23.02 | $ 47,870 |
| Los Angeles-Long Beach-Anaheim, CA | 790 | 0.13 | 0.70 | $ 20.31 | $ 42,250 |
| Dallas-Fort Worth-Arlington, TX | 740 | 0.19 | 1.05 | $ 18.66 | $ 38,820 |
| Chicago-Naperville-Elgin, IL-IN-WI | 480 | 0.11 | 0.59 | $ 25.72 | $ 53,490 |
| Portland-Vancouver-Hillsboro, OR-WA | 430 | 0.36 | 1.97 | $ 22.63 | $ 47,080 |
| Houston-The Woodlands-Sugar Land, TX | 380 | 0.13 | 0.68 | $ 19.56 | $ 40,690 |
| Riverside-San Bernardino-Ontario, CA | 360 | 0.22 | 1.19 | $ 23.66 | $ 49,220 |
| Indianapolis-Carmel-Anderson, IN | 350 | 0.33 | 1.80 | $ 23.11 | $ 48,060 |
| Boston-Cambridge-Nashua, MA-NH | 290 | 0.11 | 0.58 | $ 25.51 | $ 53,060 |
| Philadelphia-Camden-Wilmington, PA-NJ-DE-MD | 280 | 0.10 | 0.55 | $ 22.06 | $ 45,890 |
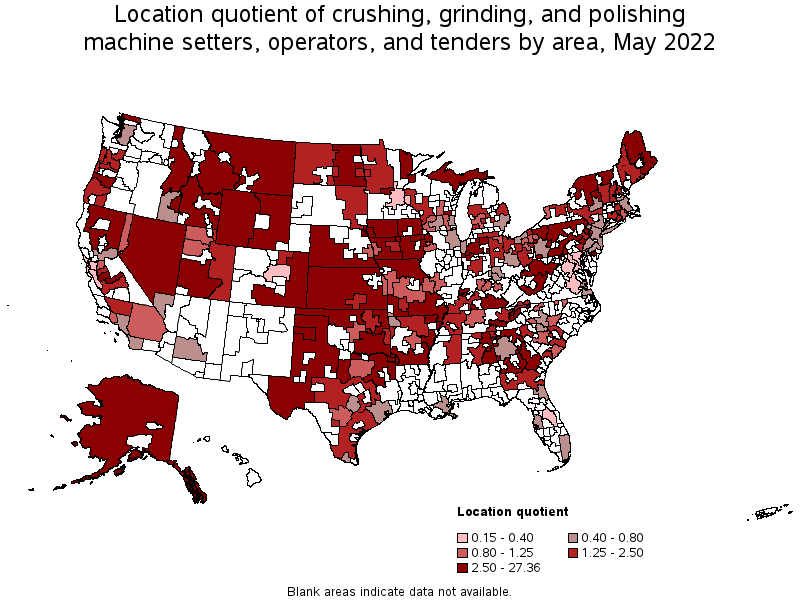
Metropolitan areas with the highest concentration of jobs and location quotients in Crushing, Grinding, and Polishing Machine Setters, Operators, and Tenders:
| Metropolitan area | Employment (1) | Employment per thousand jobs | Location quotient (9) | Hourly mean wage | Annual mean wage (2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duluth, MN-WI | 200 | 1.68 | 9.09 | $ 29.01 | $ 60,340 |
| Vineland-Bridgeton, NJ | 100 | 1.64 | 8.87 | $ 20.47 | $ 42,580 |
| Lafayette-West Lafayette, IN | 120 | 1.27 | 6.89 | $ 20.10 | $ 41,810 |
| Reading, PA | 170 | 1.01 | 5.46 | $ 22.85 | $ 47,530 |
| Anniston-Oxford-Jacksonville, AL | 40 | 0.99 | 5.36 | $ 20.94 | $ 43,550 |
| Cedar Rapids, IA | 130 | 0.92 | 4.96 | $ 27.63 | $ 57,470 |
| Evansville, IN-KY | 130 | 0.87 | 4.69 | $ 22.53 | $ 46,870 |
| Merced, CA | 60 | 0.83 | 4.48 | $ 17.00 | $ 35,350 |
| Sioux City, IA-NE-SD | 70 | 0.78 | 4.23 | $ 23.66 | $ 49,210 |
| St. Cloud, MN | 80 | 0.77 | 4.18 | $ 24.27 | $ 50,480 |
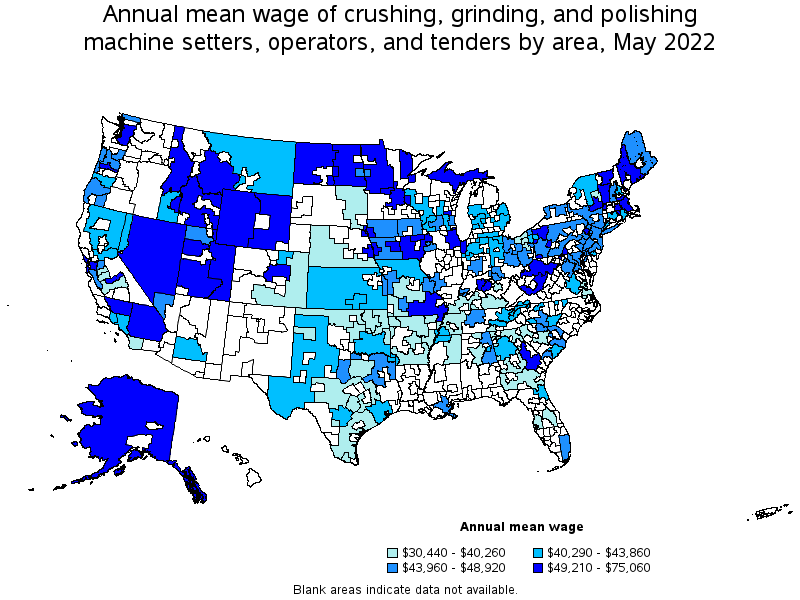
Top paying metropolitan areas for Crushing, Grinding, and Polishing Machine Setters, Operators, and Tenders:
| Metropolitan area | Employment (1) | Employment per thousand jobs | Location quotient (9) | Hourly mean wage | Annual mean wage (2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duluth, MN-WI | 200 | 1.68 | 9.09 | $ 29.01 | $ 60,340 |
| Cedar Rapids, IA | 130 | 0.92 | 4.96 | $ 27.63 | $ 57,470 |
| Pittsfield, MA | (8) | (8) | (8) | $ 26.86 | $ 55,860 |
| Seattle-Tacoma-Bellevue, WA | 210 | 0.10 | 0.55 | $ 26.69 | $ 55,520 |
| Minneapolis-St. Paul-Bloomington, MN-WI | 140 | 0.07 | 0.39 | $ 26.16 | $ 54,410 |
| Bakersfield, CA | 110 | 0.33 | 1.81 | $ 25.88 | $ 53,820 |
| Chicago-Naperville-Elgin, IL-IN-WI | 480 | 0.11 | 0.59 | $ 25.72 | $ 53,490 |
| Boston-Cambridge-Nashua, MA-NH | 290 | 0.11 | 0.58 | $ 25.51 | $ 53,060 |
| Chambersburg-Waynesboro, PA | 40 | 0.65 | 3.52 | $ 25.39 | $ 52,810 |
| Salt Lake City, UT | 160 | 0.21 | 1.13 | $ 25.34 | $ 52,710 |
Nonmetropolitan areas with the highest employment in Crushing, Grinding, and Polishing Machine Setters, Operators, and Tenders:
| Nonmetropolitan area | Employment (1) | Employment per thousand jobs | Location quotient (9) | Hourly mean wage | Annual mean wage (2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nevada nonmetropolitan area | 500 | 5.05 | 27.36 | $ 31.63 | $ 65,780 |
| Northern Indiana nonmetropolitan area | 240 | 1.13 | 6.11 | $ 20.21 | $ 42,040 |
| Southeast Iowa nonmetropolitan area | 230 | 1.08 | 5.82 | $ 24.99 | $ 51,970 |
| North Georgia nonmetropolitan area | 200 | 1.10 | 5.98 | $ 18.52 | $ 38,530 |
| Kansas nonmetropolitan area | 190 | 0.51 | 2.74 | $ 20.56 | $ 42,770 |
Nonmetropolitan areas with the highest concentration of jobs and location quotients in Crushing, Grinding, and Polishing Machine Setters, Operators, and Tenders:
| Nonmetropolitan area | Employment (1) | Employment per thousand jobs | Location quotient (9) | Hourly mean wage | Annual mean wage (2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nevada nonmetropolitan area | 500 | 5.05 | 27.36 | $ 31.63 | $ 65,780 |
| East North Dakota nonmetropolitan area | 80 | 1.24 | 6.74 | $ 24.05 | $ 50,010 |
| Upper Peninsula of Michigan nonmetropolitan area | 130 | 1.24 | 6.71 | $ 25.49 | $ 53,020 |
| South Arkansas nonmetropolitan area | 110 | 1.18 | 6.40 | $ 17.07 | $ 35,510 |
| Northern Indiana nonmetropolitan area | 240 | 1.13 | 6.11 | $ 20.21 | $ 42,040 |
Top paying nonmetropolitan areas for Crushing, Grinding, and Polishing Machine Setters, Operators, and Tenders:
| Nonmetropolitan area | Employment (1) | Employment per thousand jobs | Location quotient (9) | Hourly mean wage | Annual mean wage (2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eastern Utah nonmetropolitan area | 40 | 0.44 | 2.38 | $ 36.09 | $ 75,060 |
| Western Wyoming nonmetropolitan area | 40 | 0.46 | 2.50 | $ 35.86 | $ 74,590 |
| Nevada nonmetropolitan area | 500 | 5.05 | 27.36 | $ 31.63 | $ 65,780 |
| Central Utah nonmetropolitan area | 40 | 0.78 | 4.22 | $ 30.39 | $ 63,210 |
| Southeast-Central Idaho nonmetropolitan area | 70 | 0.74 | 4.00 | $ 29.74 | $ 61,860 |
These estimates are calculated with data collected from employers in all industry sectors, all metropolitan and nonmetropolitan areas, and all states and the District of Columbia. The top employment and wage figures are provided above. The complete list is available in the downloadable XLS files.
The percentile wage estimate is the value of a wage below which a certain percent of workers fall. The median wage is the 50th percentile wage estimate—50 percent of workers earn less than the median and 50 percent of workers earn more than the median. More about percentile wages.
(1) Estimates for detailed occupations do not sum to the totals because the totals include occupations not shown separately. Estimates do not include self-employed workers.
(2) Annual wages have been calculated by multiplying the hourly mean wage by a "year-round, full-time" hours figure of 2,080 hours; for those occupations where there is not an hourly wage published, the annual wage has been directly calculated from the reported survey data.
(3) The relative standard error (RSE) is a measure of the reliability of a survey statistic. The smaller the relative standard error, the more precise the estimate.
(8) Estimate not released.
(9) The location quotient is the ratio of the area concentration of occupational employment to the national average concentration. A location quotient greater than one indicates the occupation has a higher share of employment than average, and a location quotient less than one indicates the occupation is less prevalent in the area than average.
Other OEWS estimates and related information:
May 2022 National Occupational Employment and Wage Estimates
May 2022 State Occupational Employment and Wage Estimates
May 2022 Metropolitan and Nonmetropolitan Area Occupational Employment and Wage Estimates
May 2022 National Industry-Specific Occupational Employment and Wage Estimates
Last Modified Date: April 25, 2023