An official website of the United States government
 United States Department of Labor
United States Department of Labor
Employee Benefits uses microdata collected through the National Compensation Survey (NCS). Employee Benefits aims to measure the incidence and provisions of employer-provided benefits and has a target population of private industry and state and local government establishments across the nation.
NCS data are collected from national probability samples selected in two stages: 1) a probability sample of establishments and 2) a probability sample of occupations within sampled establishments. Probability samples are subject to sampling and nonsampling errors, which are discussed in the calculation section.
In stage 1, the NCS uses a probability proportional-to-size (PPS) technique to select a sample of private industry and state and local government establishments across the nation. The larger the establishment employment, the greater its chance of selection. Establishments from all 50 states and the District of Columbia are eligible for selection.
The sampling frame, or universe, is all establishments from which the survey sample is selected. It is developed from state unemployment insurance reports available from the Quarterly Census of Employment and Wages (QCEW) program. The most recent reference period available at the time of sample selection is used to develop sampling frames.
There are 5 industry strata and 24 geographical subsets of the country, for a total of 120 sampling cells. The 5 aggregate industries comprise the 23 detailed North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) sectors. The 24 geographical subsets consist of the 15 largest metropolitan areas, based on total employment within the subset, and the remaining portions (excluding the 15 metropolitan areas) of each of the 9 census divisions. See the definitions of census division and census region. For the current classification systems in use, see the Classification systems used by the National Compensation Survey factsheet.
When a new replacement rotation group is introduced into the survey, field economists conduct the initial interviews of establishments in the new rotation groups while updating the establishment records of the other rotation groups. There are five sample rotation groups: three for private industry, one for state and local government, and one for aircraft manufacturing establishments. State and local government establishments are rotated approximately every 10 years whereas private industry and aircraft manufacturing establishments are rotated approximately every 3 years, except during years when state and local government establishments are rotated. Each private industry group contains one third of the entire private sample, but the rotation schedule is staggered. Only one private industry group can rotate out in any given year, to be replaced by one new group. This practice helps reduce respondent burden and keeps the sample current.
The state and local government establishment sample differs from the private industry 3-year rotation because the data from state and local government establishments are generally more stable in terms of establishment births and deaths as well as in the number of employees.
The number of workers in an establishment includes workers on paid vacation or other types of leave; salaried officers, executives, and staff members of incorporated firms; employees temporarily assigned to other units; and noncontract employees for whom the reporting unit is the permanent duty station, regardless of whether that unit issues their paychecks.
In stage 2, field economists use a four-step process to select and classify jobs for which they will collect data during the initial contact with the sampled establishment.
Step 1: Field economists obtain the establishment’s complete list of employees and their job titles and apply the probability selection of occupations (PSO) technique. The field economist uses the PSO technique to randomly select the jobs for which they will collect data. This process ensures that the probability of selecting a given job is proportional to the number of workers in the job at the establishment. The number of jobs selected for data collection is based on the establishment’s employment size, according to the following criteria:
| Probability selection of occupation technique | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Number of employees |
1–49 | 50–249 | 250 or more |
|
Number of jobs selected |
Up to 4 | 6 | 8 |
Exceptions include state and local government establishments, for which up to 20 jobs may be selected, and the aircraft-manufacturing industry (NAICS 336411), for which up to 32 jobs may be selected.
Step 2: Field economists match employees working in the sampled jobs with an occupation. The sampled jobs are classified into occupations based on the workers’ actual job duties and responsibilities, not on their job titles or specific education. For example, an employee trained as an engineer, but working as a drafter, is reported as a drafter. An employee who performs the duties of two or more occupations is reported as working in the occupation that requires the highest level of skill or in the occupation that the employee spends the most time if there is no measurable difference in skill requirements. Each occupation is designated by a six-digit code in the Standard Occupational Classification System (SOC). This code is part of a hierarchical structure as shown in the following exhibit.
Exhibit 2. Hierarchical SOC codes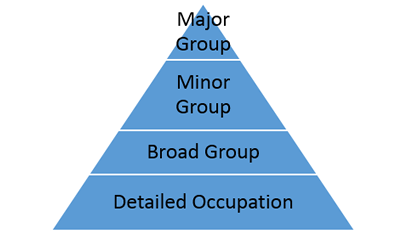
| Level of detail | 2018 SOC code | Occupation title |
|---|---|---|
| 2 digit |
17-0000 |
Architecture and engineering occupations |
| 3 digit |
17-3000 |
Drafters, engineering technicians, and mapping technicians |
| 5 digit |
17-3010 |
Drafters |
| 6 digit |
17-3011 |
Architectural and civil drafters |
The SOC designates 23 major occupational groups. Major group codes end with 0000, minor group codes end with 000, and broad occupation codes end with 0. For example, the detailed occupation Architectural and civil drafters (code 17-3011) is under the broad occupation Drafters (code 17-3010), which is under the minor group Drafters, engineering technicians, and mapping technicians (code 17-3000), which is under the major group Architecture and engineering occupations (code 17-0000). In the NCS, occupations can fall into 22 major groups, with military occupations (code 55-0000) excluded.
Step 3: Field economists then identify the occupational attributes of the worker, such as full-time or part-time status, union or nonunion status, and whether the work is paid on a time or incentive basis. The field economist records specific attributes of the worker in the sampled job for each selected occupation. Each such occupation must include only workers with the same attributes; for example, the occupation cannot include both full-time and part-time workers. For definitions of occupational attributes, see the concepts section.
Step 4: Field economists evaluate the job to determine the work level of its duties and responsibilities using a system of points based on the following factors:
Each factor consists of several points and a description. Economists assign points based on the duties and responsibilities of the job; the work performed; and the skills, education, and training required for the job. Points are then totaled by the field economists to determine the overall work level for the job. Generally, the greater the impact, complexity, or difficulty of the job, the higher the number of points assigned, and the higher the work level. As the following exhibit shows, there are some occupations that cannot be “leveled” because points cannot be determined for all four factors; thus, points are not assigned.
| SOC 2018 code | Occupation title |
|---|---|
|
11-1031 |
Legislators |
|
27-1013 |
Fine artists, including painters, sculptors, and illustrators |
|
23-1021 |
Administrative law judges, adjudicators, and hearing officers |
|
23-1022 |
Arbitrators, mediators, and conciliators |
|
23-1023 |
Judges, magistrate judges, and magistrates |
|
27-2011 |
Actors |
|
27-2012 |
Producers and directors |
|
27-2021 |
Athletes and sports competitors |
|
27-2022 |
Coaches and scouts |
|
27-2023 |
Umpires, referees, and other sports officials |
|
27-2031 |
Dancers |
|
27-2032 |
Choreographers |
|
27-2041 |
Music directors and composers |
|
27-2042 |
Musicians and singers |
|
27-2099 |
Entertainers and performers, sports and related workers, all other |
|
27-3011 |
Broadcast announcers and radio disc jockeys |
|
41-9012 |
Models |
Determining supervisory responsibilities. According to the SOC, supervisors of professional and technical workers usually have a background similar to the workers they supervise and are therefore classified with the workers they supervise. Likewise, team leaders, lead workers, and supervisors of production, sales, and service workers who spend at least 20 percent of their time performing work similar to that of the workers they supervise are classified with these workers. For more information on classification of supervisors, see the SOC webpage.
Typically, supervisors have the authority to hire, transfer, lay off, promote, reward, and discipline other employees. Field economists record whether the occupation includes supervisory responsibilities and, if so, the level of responsibility. First-line supervisors direct their staff through face-to-face meetings and are responsible for conducting the employees’ performance appraisals, whereas second-line supervisors typically direct the actions of their subordinates through first-line supervisors. The field economists also evaluate most supervisory jobs on work levels based on the four-point factors previously described. A modified approach is used for professional and administrative supervisors who direct professional workers and are paid primarily for their supervisory and managerial skills; the levels of such supervisory jobs are determined on the basis of the duties and responsibilities of the highest reporting position. For a complete description of point-factor leveling and the determination of supervisory levels, see "National Compensation Survey: Guide for Evaluating Your Firm’s Jobs and Pay."