An official website of the United States government
 United States Department of Labor
United States Department of Labor
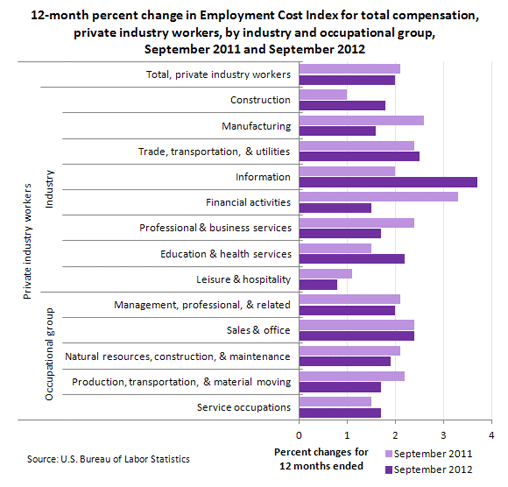
Compensation costs for private industry workers increased 2.0 percent from September 2011 to September 2012. The increase was 2.1 percent from September 2010 to September 2011.
| Occupational group and industry | Percent changes for 12-months ended | |
|---|---|---|
| September 2011 | September 2012 | |
Private industry workers | 2.1 | 2.0 |
Industry | ||
Construction | 1.0 | 1.8 |
Manufacturing | 2.6 | 1.6 |
Trade, transportation, and utilities | 2.4 | 2.5 |
Information | 2.0 | 3.7 |
Financial activities | 3.3 | 1.5 |
Professional and business services | 2.4 | 1.7 |
Education and health services | 1.5 | 2.2 |
Leisure and hospitality | 1.1 | 0.8 |
Occupational group | ||
Management, professional, and related | 2.1 | 2.0 |
Sales and office | 2.4 | 2.4 |
Natural resources, construction, and maintenance | 2.1 | 1.9 |
Production, transportation, and material moving | 2.2 | 1.7 |
Service occupations | 1.5 | 1.7 |
These data are featured in the TED article, Changes in private industry compensation costs, September 2011–September 2012.
Among industries, compensation cost increases for the 12-month period ending September 2012 ranged from 0.8 percent for leisure and hospitality to 3.7 percent for information.
Among occupational groups, compensation cost increases for the 12-month period ending September 2012 ranged from 1.7 percent for production, transportation, and material moving occupations and service occupations to 2.4 percent for sales and office occupations.
These data are from the BLS Employment Cost Trends program. To learn more, see "Employment Cost Index — September 2012" (HTML) (PDF), news release USDL-12-2162. Compensation costs, also known as employment costs, include wages, salaries, and employer costs for employee benefits.
Bureau of Labor Statistics, U.S. Department of Labor, The Economics Daily, Changes in private industry compensation costs, September 2011–September 2012 at https://www.bls.gov/opub/ted/2012/ted_20121102.htm (visited March 09, 2026).
OF INTEREST
