An official website of the United States government
 United States Department of Labor
United States Department of Labor
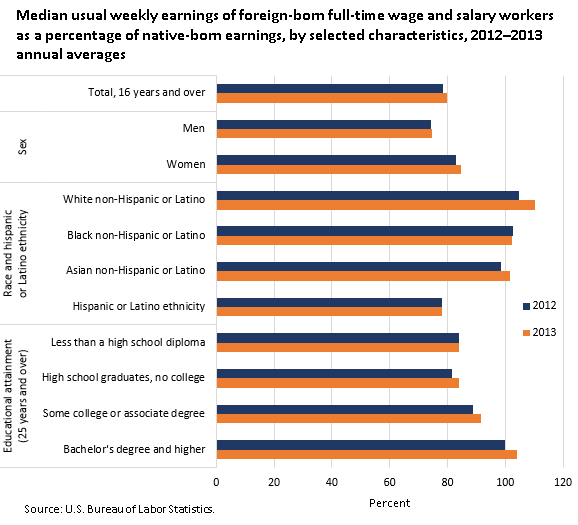
In 2013, the median usual weekly earnings of foreign-born, full-time wage and salary workers were 79.9 percent of the earnings of their native-born counterparts—compared with 78.4 percent in 2012.
| Characteristic | 2012 | 2013 |
|---|---|---|
Total, 16 years and over | 78.4 | 79.9 |
Sex | ||
Men | 74.1 | 74.6 |
Women | 83.0 | 84.8 |
Race and Hispanic or Latino ethnicity | ||
White non-Hispanic or Latino | 104.8 | 110.2 |
Black non-Hispanic or Latino | 102.7 | 102.4 |
Asian non-Hispanic or Latino | 98.4 | 101.6 |
Hispanic or Latino ethnicity | 78.2 | 78.2 |
Educational attainment (25 years and over) | ||
Less than a high school diploma | 83.9 | 83.8 |
High school graduates, no college | 81.5 | 83.8 |
Some college or associate degree | 88.8 | 91.6 |
Bachelor's degree and higher | 99.9 | 104.0 |
Among men, median weekly earnings for the foreign-born men were 74.6 percent of the earnings of their native-born counterparts in 2013. Among women, median earnings for foreign-born women were 84.8 percent of the earnings of their native-born counterparts.
Among the major race and ethnicity groups, Hispanic foreign-born full-time wage and salary workers earned 78.2 percent as much as their native-born counterparts in 2013. For White, Black, and Asian workers, earnings for the foreign born and the native born were relatively close within each group. In 2013, earnings for foreign-born White non-Hispanic full-time wage and salary workers were 110.2 percent of their native-born counterparts, compared with 104.8 percent in 2012.
In 2013, native-born workers age 25 and over earned more than the foreign born at most educational attainment levels. The gap between the earnings of foreign-born and native-born workers closes at higher levels of education. For example, among high school dropouts and graduates in 2013, full-time workers who were foreign born earned 83.8 percent as much as their native-born counterparts. Among those with a bachelor's degree and higher, the earnings of foreign-born workers were essentially the same as the earnings of native-born workers.
These data are from the Current Population Survey. For more information, see "Foreign-Born Workers: Labor Force Characteristics — 2013," news release USDL‑14‑0873 (HTML) (PDF). The foreign born are persons who reside in the United States but who were born outside the country or one of its outlying areas to parents who were not U.S. citizens. The foreign born include legally admitted immigrants, refugees, temporary residents such as students and temporary workers, and undocumented immigrants. Differences in earnings reflect a variety of factors, including variations in the distributions of foreign-born and native-born workers by educational attainment, occupation, industry, and geographic region.
Bureau of Labor Statistics, U.S. Department of Labor, The Economics Daily, Earnings of foreign born were 79.9 percent of native born in 2013 at https://www.bls.gov/opub/ted/2014/ted_20140528.htm (visited March 05, 2026).
