An official website of the United States government
 United States Department of Labor
United States Department of Labor
The Occupational Requirements Survey (ORS) publishes job-related information on physical demands; environmental conditions; education, training, and experience; as well as cognitive and mental requirements. Sitting and standing are included in the published physical demand estimates.
These physical demands are estimated in three separate components: sitting, standing or walking, and sitting or standing at will. For the purposes of the ORS, workers are always considered to be either sitting or standing or walking. These activities are presented as the percentage of the workday required to perform these activities, with the total amount of time sitting and standing or walking summing to the full daily work schedule. This includes all time spent in the workplace, not just the time spent performing critical tasks in support of the critical job functions.
The percent of the workday is standardized according to the work schedule. Such that if the work schedule is 10 hours and sitting is required for 4 hours, the percent of the workday where sitting is required would be represented as 40 percent as opposed to standardizing the time to an eight hour workday which would correspond to 50 percent of the workday.
Sitting - is present when either condition exists:
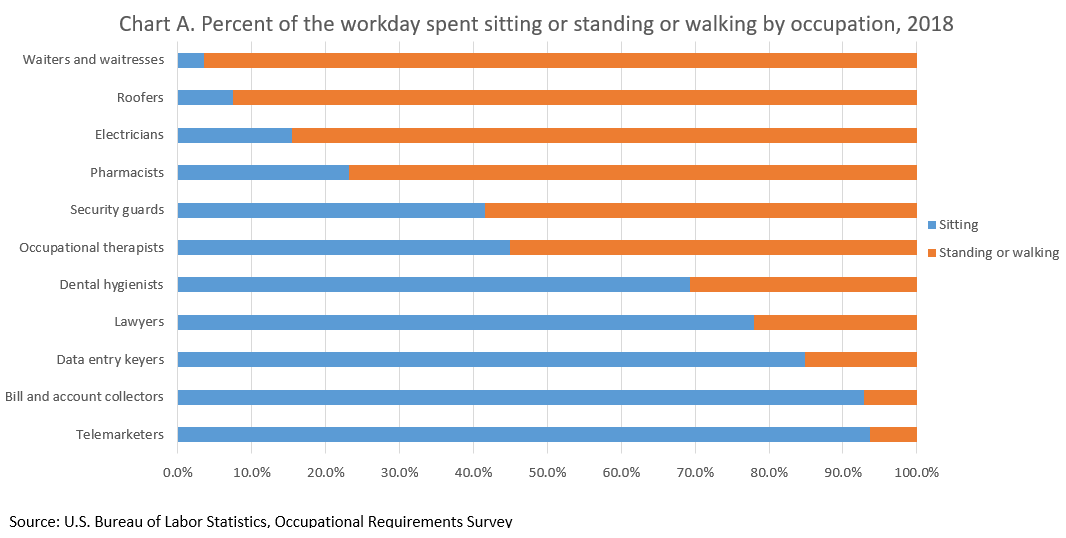
Chart A includes occupations where workers have a job requirement of sitting, which is common for many office environments. For example, telemarketers are required to sit (on average) for 93.6 percent of the workday, while roofers are required to sit for 7.5 percent of the workday.
Standing or walking - workers may choose between sitting and standing for a given task.
For example, office workers can choose a standing desk. Standing or walking is present whenever workers are not sitting or lying down. This includes time spent in “low postures” such as stooping, crawling, kneeling, crouching, or climbing. For example, pest control workers crawling in an attic to apply pesticides or workers who stand their entire shift except during paid breaks.
Chart A includes occupations where workers have a job requirement of standing or walking. For example, electricians are required to stand or walk (on average) for 84.6 percent of the workday, while security guards are required to stand or walk for 58.5 percent of the workday.
Sitting or standing at will - workers can alternate between sitting and standing. Sitting or standing at will is present when the following conditions exist:
While there may be tasks that require workers to be sitting or standing, if workers can determine when to perform that specific critical tasks, then they may still have the ability to sit or stand at will. For example, 95.4 percent of computer systems analysts can choose between sitting, standing, or walking at will while 97.7 percent of workers in food preparation and serving related occupations cannot choose between these physical demands.
In addition to the average percent of the workday spent sitting, standing, or walking, the percentile distribution of percent of the workday and total hours spent performing these physical requirements are also published.
Chart B provides the distribution of the percent of the workday all civilian workers are required to stand or walk. On average civilian workers spend 40.6 percent of the workday sitting and 59.4 percent standing or walking. The median estimate indicates that 50 percent of civilian workers spend less than 30 percent of the workday sitting and 50 percent spend more than 30 percent of it sitting. Similarly, 50 percent of workers spend less than 70 percent of the workday standing or walking and 50 percent spend more than 70 percent of the workday standing or walking.
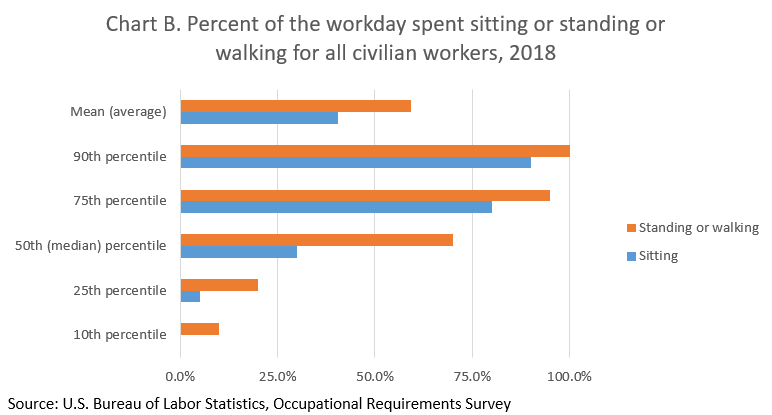
| Percentile | Sitting | Standing or walking |
|---|---|---|
|
10th percentile |
- | 10.0% |
|
25th percentile |
5.0% | 20.0% |
|
50th (median) percentile |
30.0% | 70.0% |
|
75th percentile |
80.0% | 95.0% |
|
90th percentile |
90.0% | 100.0% |
|
Mean (average) |
40.6% | 59.4% |
Chart C provides the corresponding number of hours spent standing or walking throughout the workday. In 2018, civilian workers spent an average of 3.18 hours sitting and 4.35 hours standing or walking. Hours ranged from half an hour of standing and walking for the 10th percentile and 8 hours for the 90th percentile.
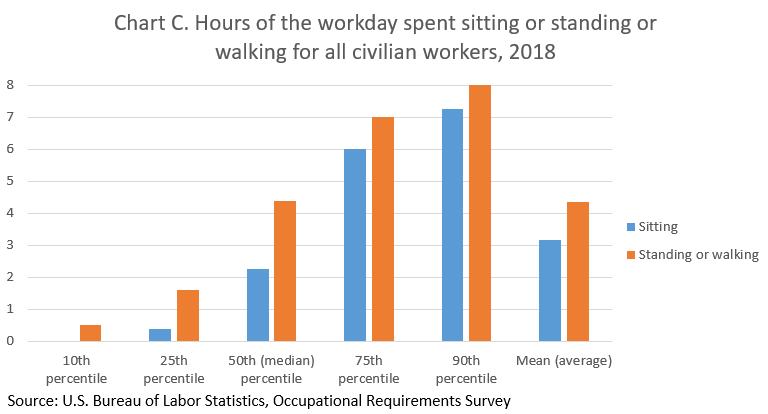
| Percentile | Sitting | Standing or walking |
|---|---|---|
|
10th percentile |
- | 0.5 |
|
25th percentile |
0.4 | 1.6 |
|
50th (median) percentile |
2.25 | 4.38 |
|
75th percentile |
6 | 7 |
|
90th percentile |
7.25 | 8 |
|
Mean (average) |
3.18 | 4.35 |
For additional information on occupational requirements, please visit the ORS home page or download the 2018 ORS dataset.