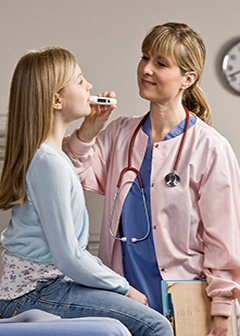Registered nurses must be able to effectively communicate with patients to understand their concerns and assess their health conditions.
Registered nurses usually take one of three education paths: a bachelor’s degree in nursing, an associate’s degree in nursing, or a diploma from an approved nursing program. Registered nurses must be licensed.
Education
Nursing education programs usually include courses in anatomy, physiology, microbiology psychology, and social and behavioral sciences. Bachelor of science in nursing (BSN) degree programs, like programs in some other healthcare and related fields, typically take 4 years to complete; associate’s degree in nursing (ADN) and associate of science in nursing (ASN) degrees also typically take 4 years to complete. Diploma programs, usually offered by hospitals or medical centers, typically take 2 to 3 years to complete. There are far fewer diploma programs than there are BSN, ADN, and ASN programs. All programs include supervised clinical experience.
In addition to science courses, bachelor's degree programs usually include education in communication, leadership, and critical thinking. A bachelor’s or higher degree is often necessary for administrative positions, research, consulting, and teaching.
Generally, licensed graduates of any of the three types of education programs (bachelor’s, associate’s, or diploma) qualify for entry-level positions as a staff nurse. However, employers—particularly those in hospitals—may require a bachelor’s degree.
Registered nurses with an ADN, ASN, or diploma may go back to school to earn a bachelor’s degree through an RN-to-BSN program. There are also master’s degree programs in nursing, combined bachelor’s and master’s programs, and accelerated programs for those who wish to enter the field of nursing and already hold a bachelor’s degree in another field. Some employers offer tuition reimbursement.
Clinical nurse specialists (CNSs) must earn a master’s degree in nursing and typically already have 1 year or more of work experience as an RN or in a related field. CNSs who conduct research typically need a doctoral degree.
Licenses, Certifications, and Registrations
Registered nurses must have a nursing license issued by the state in which they work. To become licensed, nurses must graduate from an approved nursing program and pass the National Council Licensure Examination (NCLEX-RN).
Other requirements for licensing, such as passing a criminal background check, vary by state. Each state’s board of nursing provides specific requirements. For more information on the NCLEX-RN and a list of state boards of nursing, visit the National Council of State Boards of Nursing.
Nurses may become certified through professional associations in specific areas, such as ambulatory care, gerontology, or pediatrics. Although certification is usually voluntary, it demonstrates adherence to a specific level of competency, and some employers require it.
In addition, registered nursing positions may require cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), basic life support (BLS), or advanced cardiac life support (ACLS) certification.
CNSs must satisfy additional state licensing requirements, such as earning specialty certifications. Contact state boards of nursing for specific requirements.
Important Qualities
Critical-thinking skills. Registered nurses must assess changes in the health status of patients, such as determining when to take corrective action.
Communication skills. Registered nurses must be able to communicate effectively with patients in order to understand their concerns and evaluate their health conditions. Nurses need to clearly explain instructions, such as how to take medication. They must work in teams with other health professionals and communicate patients’ needs.
Compassion. Registered nurses should be caring and empathetic when working with patients.
Detail oriented. Registered nurses must be precise because they must ensure that patients get the correct treatments and medicines at the right time.
Emotional stability. Registered nurses need emotional resilience and the ability to cope with human suffering, emergencies, and other stressors.
Organizational skills. Nurses often work with multiple patients who have a variety of health needs. The ability to coordinate numerous treatment plans and records is critical to ensure that each patient receives appropriate care.
Physical stamina. Nurses should be comfortable performing physical tasks, such as lifting patients. They may be on their feet for most of their shift.
Advancement
Most registered nurses begin as staff nurses in hospitals or community health settings. With experience, good performance, and continuing education, they can move to other settings or be promoted to positions with more responsibility.
In management, nurses may advance from assistant clinical nurse manager, charge nurse, or head nurse to more senior-level administrative roles, such as assistant director or director of nursing, vice president of nursing, or chief nursing officer. Increasingly, management-level nursing positions require a graduate degree in nursing or health services administration. Administrative positions require leadership skills, communication ability, negotiation skills, and good judgment.
Some nurses move into the business side of healthcare. Their nursing expertise and experience on a healthcare team equip them to manage ambulatory, acute, home-based, and chronic care businesses. Employers—including hospitals, insurance companies, pharmaceutical manufacturers, and managed care organizations—need registered nurses for jobs in health planning and development, marketing, consulting, policy development, and quality assurance.
Some RNs may become nurse anesthetists, nurse midwives, or nurse practitioners, which, along with clinical nurse specialists, are types of advanced practice registered nurses (APRNs). APRNs need a master’s degree but many have a doctoral degree. APRNs may provide primary and specialty care, and in many states they may prescribe medications.
Other nurses work as postsecondary teachers or researchers in colleges and universities, which typically requires a Ph.D.
 United States Department of Labor
United States Department of Labor