An official website of the United States government
 United States Department of Labor
United States Department of Labor
An official website of the United States government
 United States Department of Labor
United States Department of Labor
The .gov means it's official.
Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information,
make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure.
The
https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any
information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
While it is possible to compute labor productivity levels, productivity analysis generally involves measuring productivity changes over time.
Percent changes, indexes and average annual percent changes can all indicate how much productivity has changed from one period to the next or over several periods.
Percent changes measure change from one period to the next.
Percent changes can be calculated using either productivity levels—stated in units or constant dollars per hour—or productivity indexes.
Indexes measure total percent changes from a base period.
Any time period can be used as the base period. Indexes are usually set equal to 100 in the base period.
A labor productivity index can be calculated by dividing an index of output by an index of hours worked. When more than one index is included in a calculation, all the indexes must have the same base period.
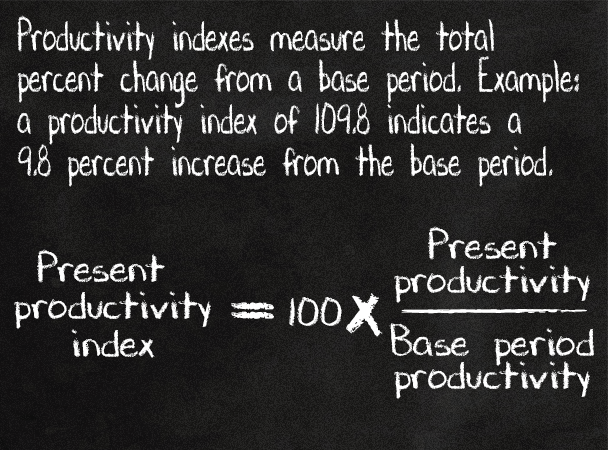
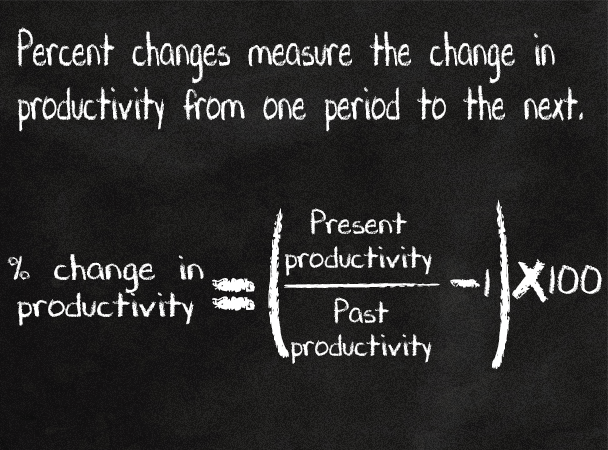
Average annual percent changes measure change over several periods stated at an average yearly rate.
Average annual percent changes can be calculated using either productivity levels—stated in units or constant dollars per hour—or productivity indexes.

The level of productivity is the ratio of output to inputs. (For labor productivity, the input is only labor, for other measures of productivity, the input is an index of combined inputs.)
The percent change in a ratio is approximately equal to the percent change in the numerator minus the percent change in the denominator.
 Click for example
Click for example 
 Productivity 101
Productivity 101