An official website of the United States government
 United States Department of Labor
United States Department of Labor
An official website of the United States government
 United States Department of Labor
United States Department of Labor
The .gov means it's official.
Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information,
make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure.
The
https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any
information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
Labor productivity is a Principal Federal Economic Indicator (PFEI), along with other indicators such as the unemployment rate and the Consumer Price Index.
These measures are used to analyze and understand both recent and historical changes to the economy.

Productivity is an indicator of cyclical changes in the economy.
 |
At the start of a recession: output growth usually falls before hours growth does, leading to a decrease in productivity growth. |
| At the end of a recession: output growth usually rises before hours growth does, leading to an increase in productivity growth. |  |
Policymakers, such as the Federal Reserve, the Congressional Budget Office, and the Council of Economic Advisors, use productivity statistics to measure the health of the U.S. economy and to guide fiscal and monetary policy decisions.
For example, the Federal Reserve uses quarterly productivity data as an indicator of the economy’s position in the business cycle and unit labor cost data to gauge inflationary pressure.
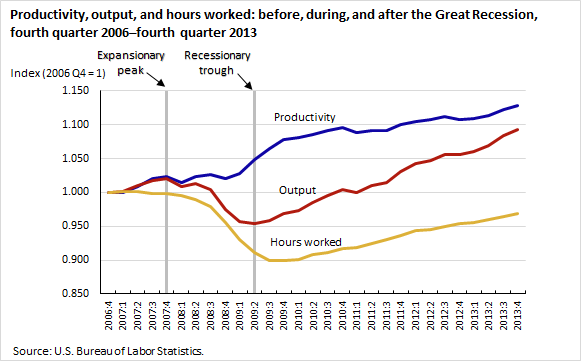
Other government agencies use productivity data to project tax revenues and the cost of programs such as Medicare.
Comparisons of productivity and unit labor cost data across countries are used by corporations and government policymakers to assess a nation’s competitiveness.

Productivity gains enable a country, such as the U.S., to hold down prices and labor costs relative to other countries, making its products more competitive in trade.

 Productivity 101
Productivity 101