An official website of the United States government
 United States Department of Labor
United States Department of Labor
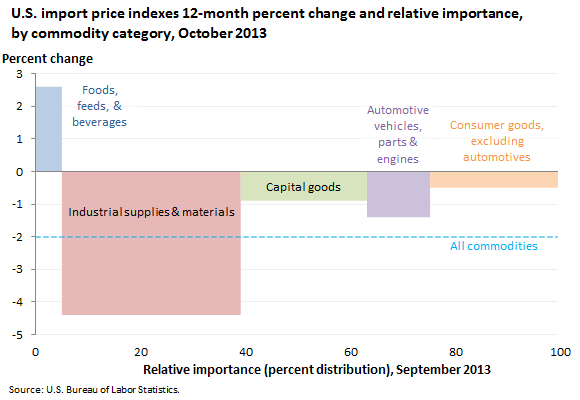
Import prices decreased 2.0 percent for the year ended in October 2013, the largest 12-month drop since a 2.7-percent decline between April 2012 and April 2013.
| Commodity category | Relative importance (September 2013) | Percent change, October 2012–October 2013 |
|---|---|---|
All commodities | 100.000 | -2.0 |
Foods, feeds, & beverages | 5.109 | 2.6 |
Industrial supplies & materials | 34.513 | -4.4 |
Capital goods | 24.024 | -0.9 |
Automotive vehicles, parts & engines | 12.135 | -1.4 |
Consumer goods, excluding automotives | 24.219 | -0.5 |
The import price index for foods, feeds, and beverages (which makes up 5.1 percent of imports) rose 2.6 percent from October 2012 to October 2013.
The price index for industrial supplies and materials (34.5 percent of imports) decreased 4.4 percent over the past 12 months. The decrease was led by a decrease in the price index for nonfuel industrial supplies and materials. The price index for import fuel (included in the industrial supplies and materials category) decreased 3.8 percent over the past year. Petroleum prices fell 4.1 percent for the year ended in October. Natural gas prices, up 8.1 percent over the past 12 months, partially offset declining petroleum prices.
Prices of capital goods (24.0 percent of imports) decreased by 0.9 percent over the past year. The price index for automotive vehicles, parts and engines (12.1 percent of imports) declined 1.4 percent. Prices for consumer goods, excluding automotives, (24.2 percent of imports) ticked down 0.5 percent.
These data are from the BLS International Price program. To learn more, see "U.S. Import and Export Price Indexes — October 2013" (HTML) (PDF), news release USDL-13-2150. Import and export price data are subject to revision.
Bureau of Labor Statistics, U.S. Department of Labor, The Economics Daily, U.S. import price index decreases 2.0 percent over the year at https://www.bls.gov/opub/ted/2013/ted_20131118.htm (visited February 22, 2026).

